Thanks to innovations in machine learning algorithms and rapid advancements in computing hardware, many GIS and remote sensing tasks can now be done more swiftly and accurately. Traditionally time-consuming processes, such as manually digitizing building footprints or generating land cover maps, can now be completed at the click of a button with the help of ready-to-use geospatial deep learning models.
Esri has been developing support for deep learning in ArcGIS for a while now, announcing the release of its first set of ready-to-use geospatial AI models on ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World in October 2020. Today, there are 12 pre-trained deep learning models available for ArcGIS Pro users.
Here, we list the top 5 machine learning models that you could use to automate the task of digitizing and extracting geographical features from satellite imagery and point cloud datasets:
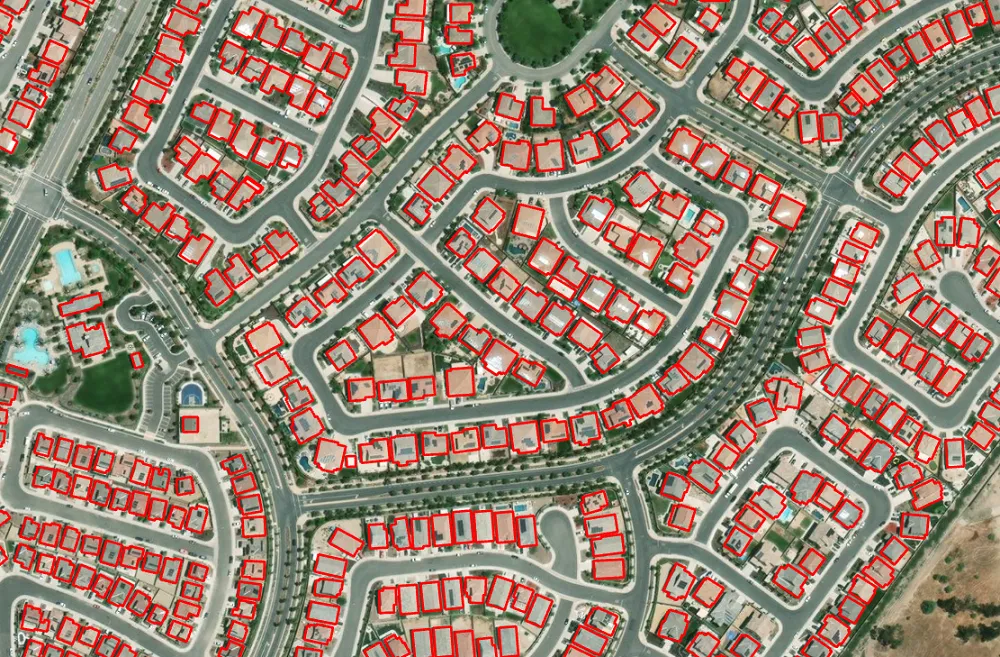
Building Footprint Extraction
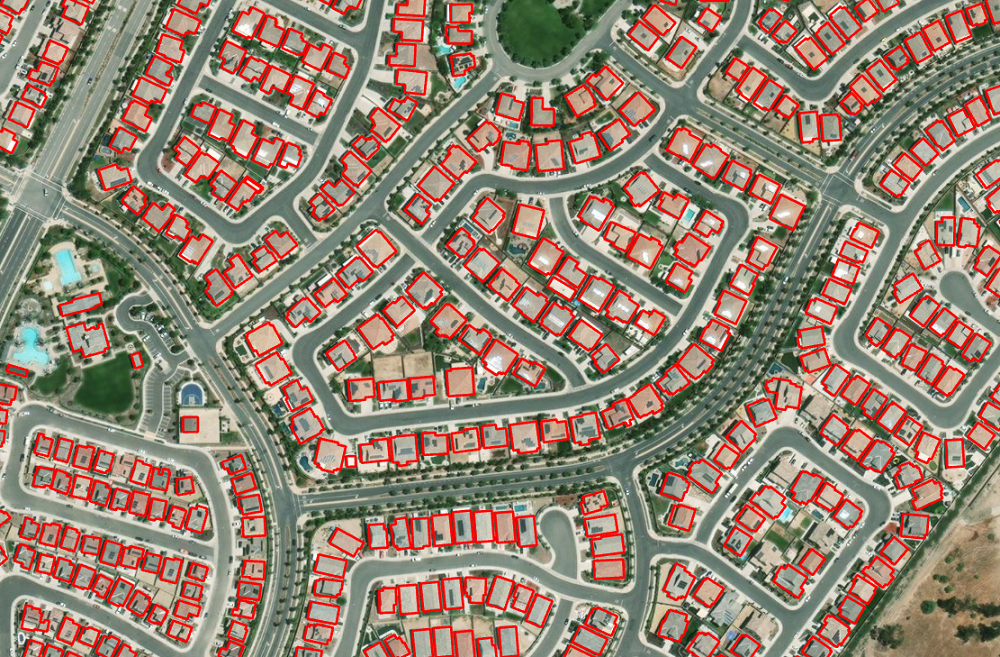

Building footprint layers are useful for several applications, including preparing base maps and analysis workflows for urban planning and development, insurance, taxation, change detection, and infrastructure planning. This deep learning model from Esri can extract building footprints from high-resolution (10–40 cm) imagery in a jiffy, even if the buildings are located close to each other.
Road Extraction
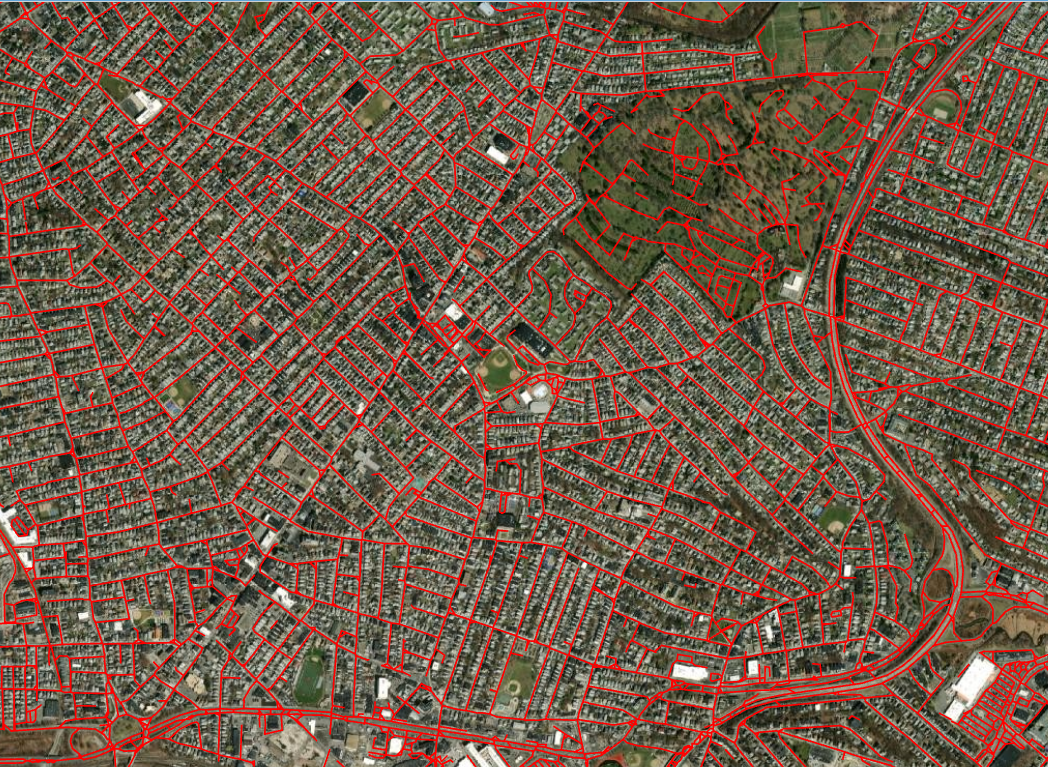
It’s no secret that digitizing and updating the road infrastructure can be incredibly time-consuming. And yet, roads are one of the primary GIS layers required by any government agency for infrastructure planning, urban planning, and developing an effective, efficient information model. The great thing about Esri’s Road Extraction deep learning model is that it is trained to extract connected road segments – and not fragmented ones – from satellite imagery. The model even recognizes dirt roads and well pad access roads.
Land Cover Classification
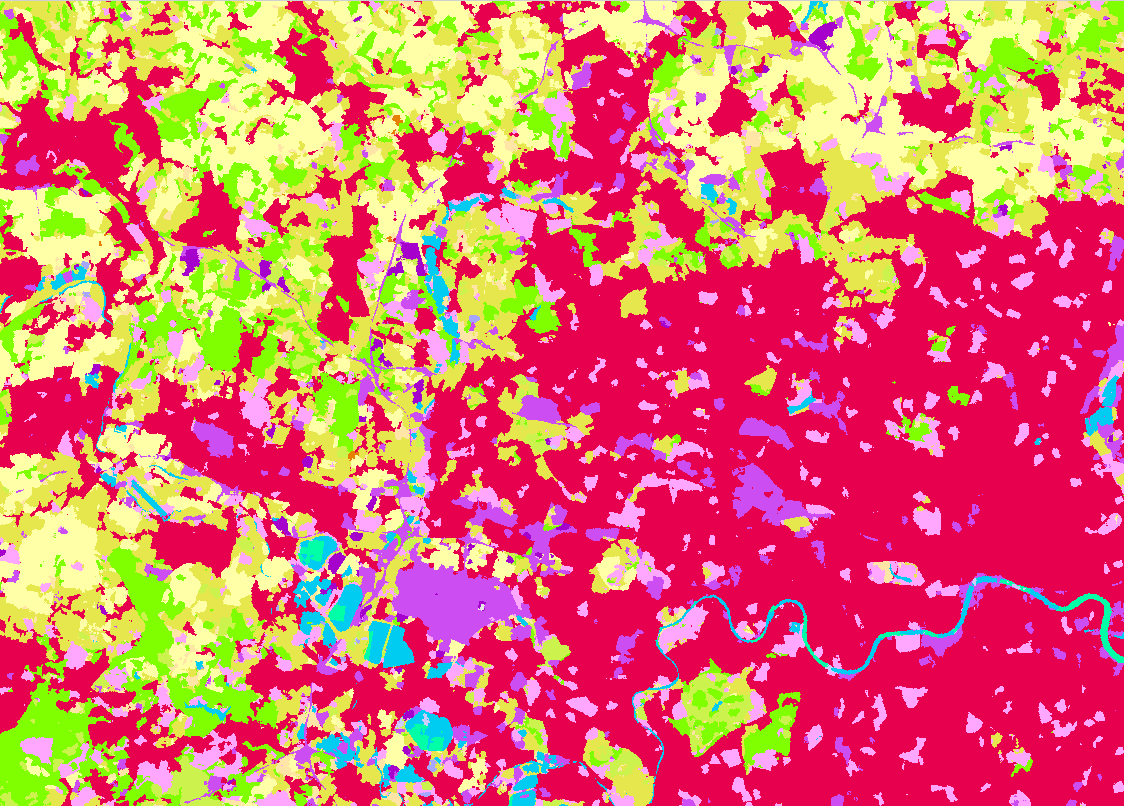
Land cover maps are essential for understanding urban planning, resource management, change detection, agriculture, and several other applications in which information related to the earth’s surface is required. Esri’s Land Cover Classification deep learning models are trained on Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 imagery datasets to ensure superior results in Europe and the United States.
This model can also be used to determine land cover change detection, such as that caused by a wildfire, or to see the growing urbanization.
Human Settlements
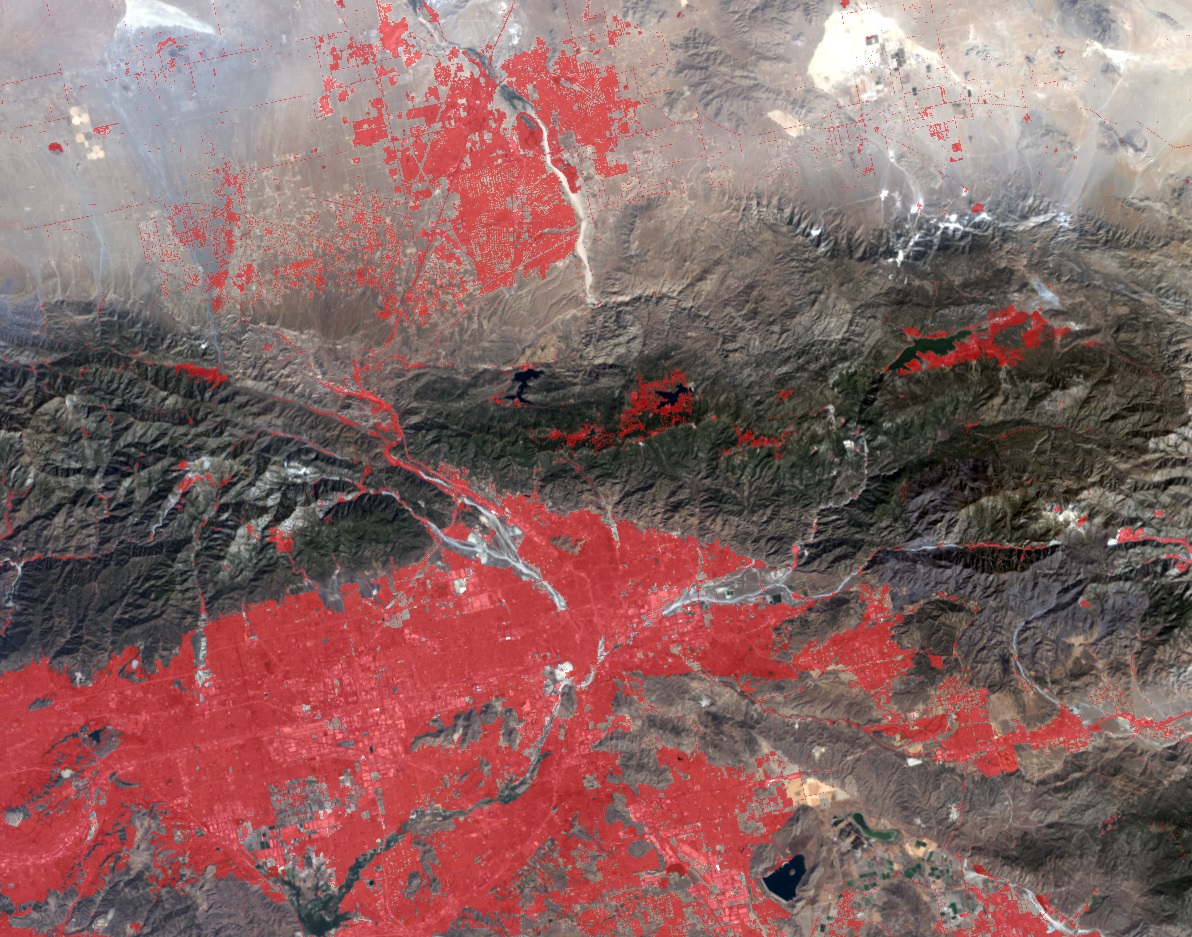

Understand regional or global growth patterns, population distribution, resource management, change detection, et al, necessitates the creation of small-scale maps derived from relatively lower resolution satellite imagery. Esri’s pre-trained Human Settlements machine learning model works on both Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 imagery and can be used to identify unmapped communities to ensure impeccable vaccination planning.
License Plate or Face Blurring
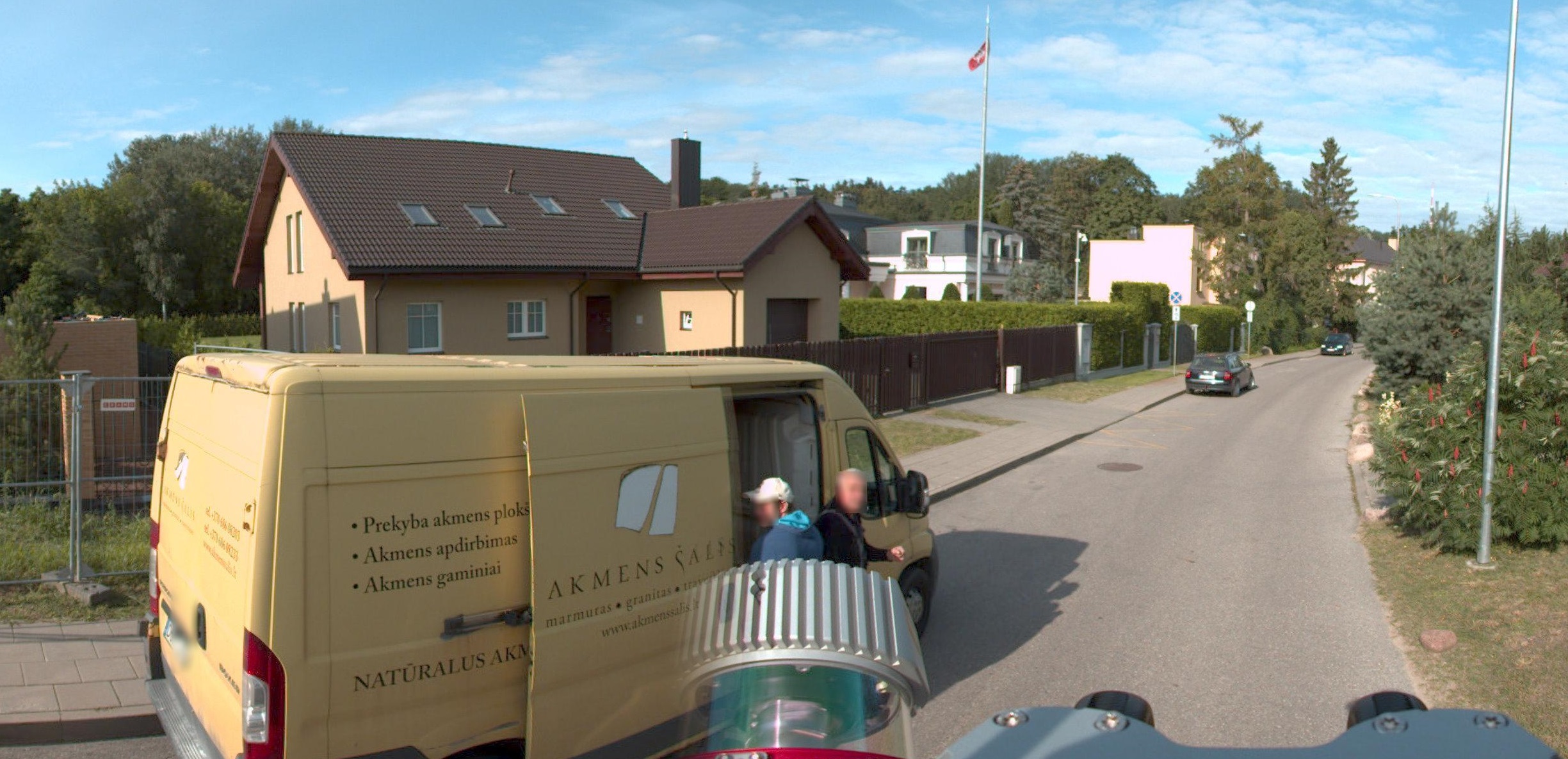

If you need to anonymize or redact faces and car license plates from street-view imagery to safeguard the privacy rights of users, Esri’s ready-to-use deep learning models can help you to prevent the identification of people and vehicles.
Some other deep learning models by Esri that may interest you include powerline classification, tree point classification, shipwreck detection, and windows and door extraction.








