How can satellite data add value for different construction stakeholders?
Part 2 in our EO Hub construction series
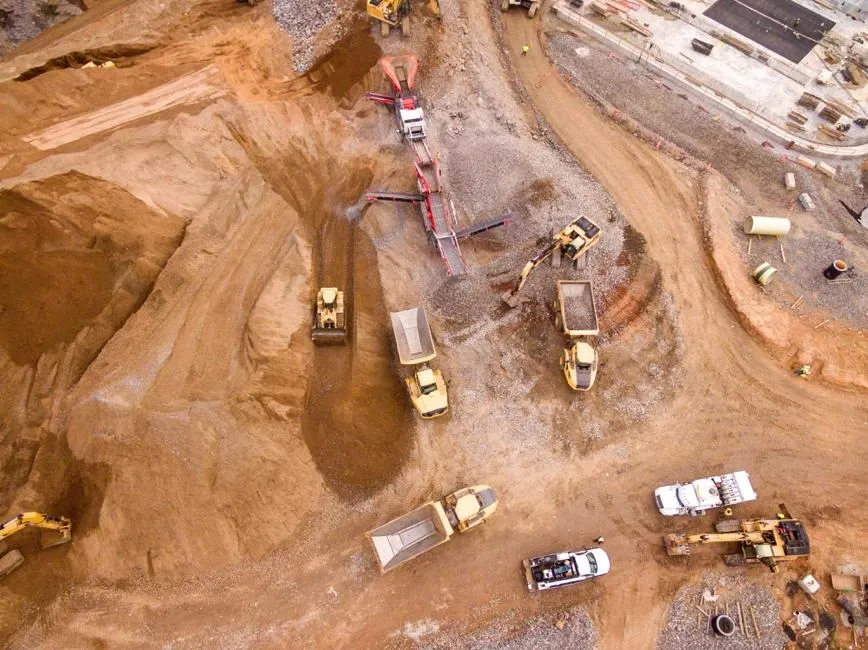
The construction industry, traditionally one of the slowest to embrace digital changes, has been making notable strides in recent years, with increasing interest in drone technology. But while UAVs are now commonly seen over modern construction sites, satellite data has not yet been adopted in any meaningful way.
However, the tool is emerging as a potential game-changer when it comes to large-scale and mega projects: while a few simple buildings can be easily monitored on foot, expansive mega projects, often spread over hundreds of kilometres, pose a unique challenge, exceeding the capabilities of traditional mapping or even drone technologies.
In this, the second in our three-part series on the use of satellite data in construction, we look in more detail at the myriad ways construction stakeholders can leverage satellite data across the entire construction lifecycle of these enormous sites.
What kind of satellite data can be used by the construction industry?
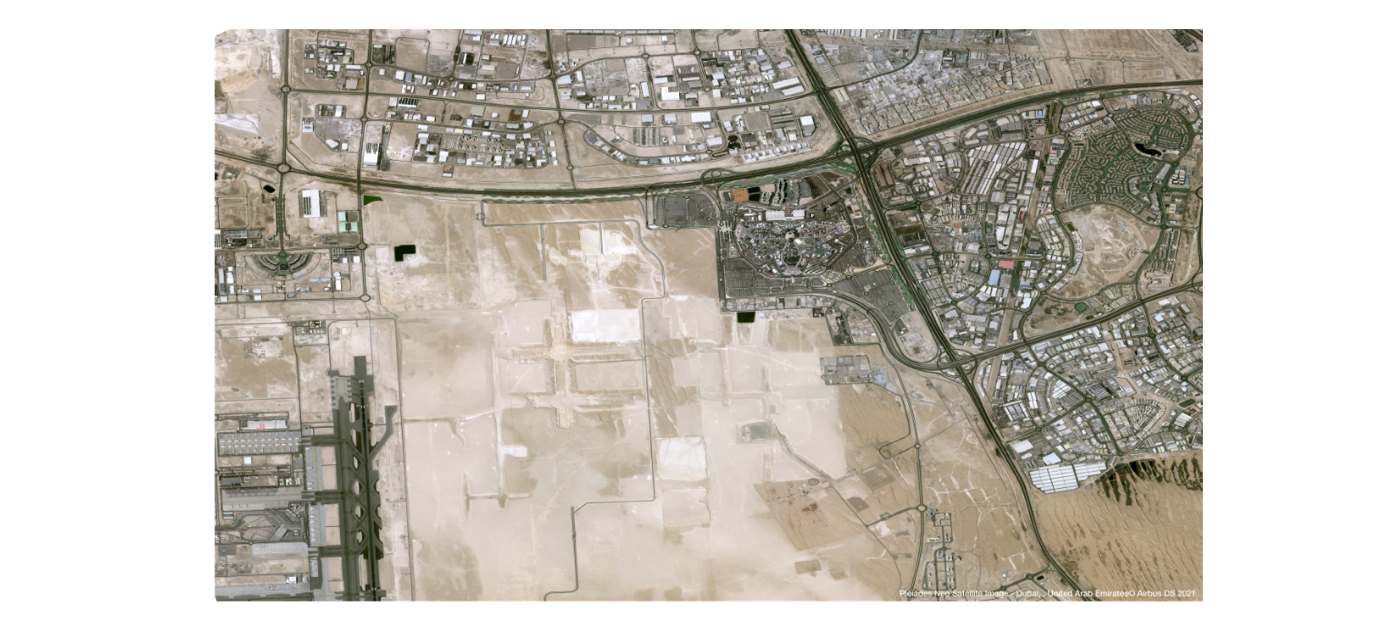
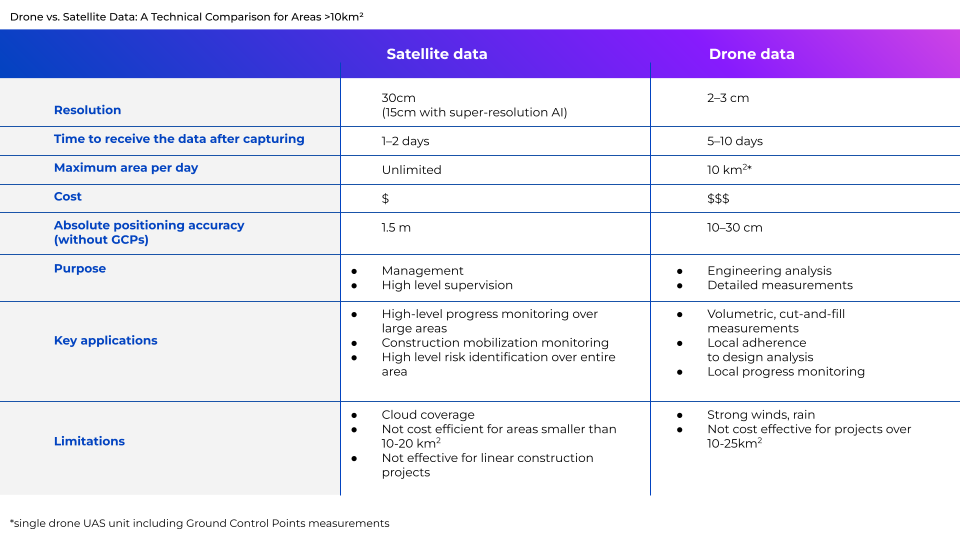
When it comes to satellite imagery for construction, there is a simple rule: the higher the resolution, the better. And with 30cm resolution now available from several satellite providers, the data available is more precise than ever. Furthermore, this can be enhanced to 15cm by super resolution, which, although it cannot add any detail missing from the original image, significantly improves its readability by both humans and machines.
However, there are other facets to satellite data which improve its usability for construction stakeholders. Among the most notable are improved elevation accuracy and orthorectification.

0.5 elevation accuracy: The degree of accuracy in measuring elevations is crucial for understanding topographical variations across large construction sites, and satellite data is now accurate to within half a meter (0.5m). This degree of accuracy ensures that designers, architects, engineers, and contractors have a reliable and nuanced understanding of the terrain. This facilitates more informed decisions in the project planning and design phases, allows for precise calculation of earthwork quantities, better predictions of drainage patterns, and a detailed understanding of the site’s environmental and geotechnical conditions. Moreover, with the advent of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and other digital tools, highly accurate elevation data becomes even more vital, as it leads directly to a more realistic representation.
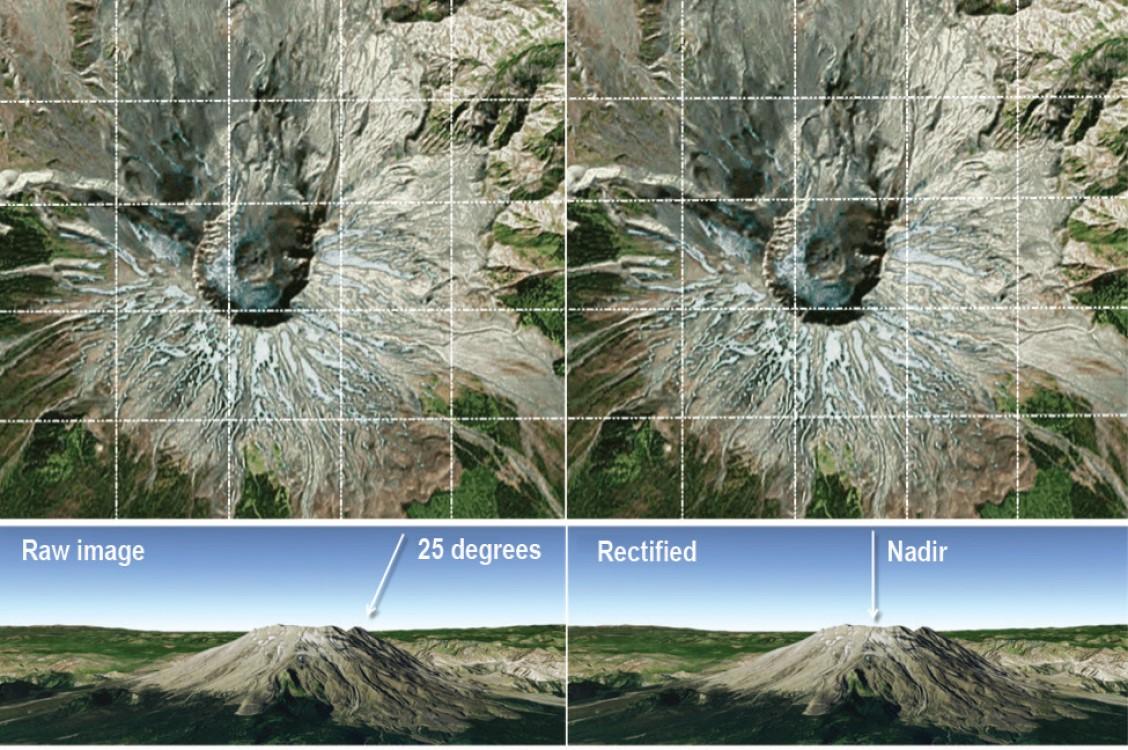
Orthorectified imagery: Orthorectification is a process that removes the effects of image distortion due to perspective, tilt, and terrain relief. It is created by calculating the nadir view of every pixel in the image, with the resulting ‘orthophotos’ having the aesthetics of a photograph and the positional accuracy of a map. Orthorectified images always show the earth’s surface from the same nadir angle, which is critical for change detection and comparing timeseries of satellite data with each other, and have a uniform scale, essential for mapping and monitoring. Marketplaces like UP42 offer orthorectified images as well as orthorectification services.
Satellite Data adds value for every stakeholder, throughout the construction lifecycle
It’s an observed trend that construction projects—especially large-scale and mega projects—often experience budget and cost overruns. Such projects are typically very ambitious in their scope, and pose inherent management challenges due to both their engineering complexity and sheer geographical spread. Without comprehensive data and appropriate analytical methods, effective management becomes an uphill task. Continuous situational awareness is therefore essential—and in this context, satellites have the potential to add transformative capabilities to the construction sector as a high-level management tool. They can also be complemented by the use of drones, which remain a key engineering instrument for capturing detailed measurements.
However, it’s important to note that neither technology can entirely replace the precision and expertise of land surveyors and on-site supervision. Combining traditional methods with modern data collection tools ensures stakeholders are equipped with current information, facilitating prompt and informed decision-making. This proactive approach aids in risk mitigation, ensuring projects remain on schedule and within budget.
This table illustrates how satellite data comes into play for different stakeholders at different stages of the construction lifecycle:
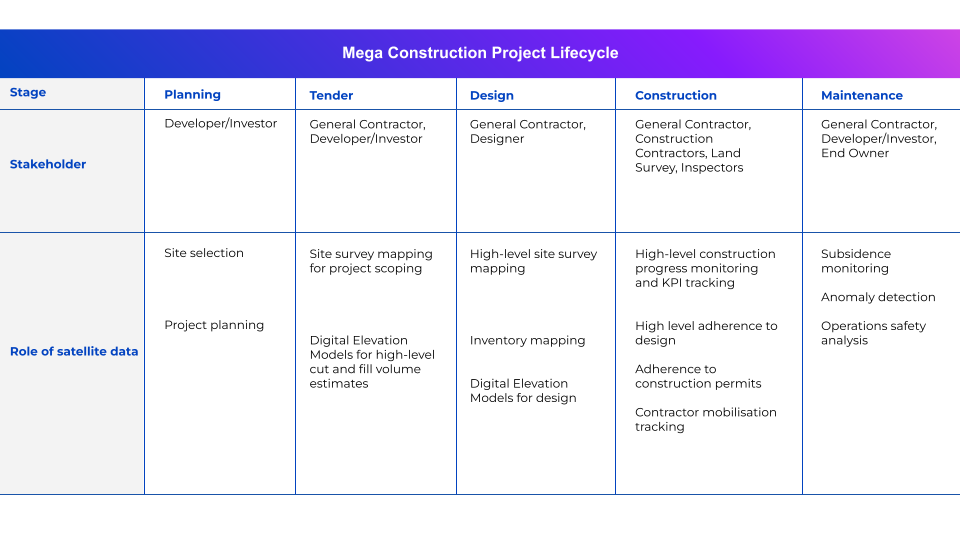
For developers and investors, satellite data presents a wealth of accurate, detailed information about a site and its surroundings, in an easily-readable visual format. Developers can therefore make informed decisions regarding a project’s feasibility—and its potential profitability. As the project unfolds, these stakeholders can employ satellite data to ensure that progress is in line with budget and timeline, aiding in the early identification of potential hiccups and minimizing financial risk.
General contractors can incorporate near-real-time satellite data into their management process to help them coordinate construction activities, such as the movement and placement of equipment and materials, with precision. Furthermore, they can monitor the ongoing progress and quickly spot any deviations or issues. This results in enhanced productivity, cost efficiencies, and improved quality control.
For designers, including architects and engineers, satellite data can be an unparalleled tool for site analysis, shedding light on factors including topography, land use, environmental nuances, and surrounding infrastructure. This wealth of information can be instrumental in helping designers draw up plans for constructions that work in harmony with the existing environment.
Construction companies could derive similar immediate benefits from satellite data to general contractors, with applications in project management and quality control. However, these companies can also utilise satellites in their long-term strategic planning, whether scoping out potential locations for future projects, tracking market changes, or post-completion assessment of processes and projects.
Land surveyors may be able to use satellite data to minimize dependence on exhaustive and costly ground surveys, as high-definition satellite imagery can provide intricate details about a site’s topography. However, it’s essential to bear in mind that satellite data, while hugely valuable, might not always serve as a complete substitute for on-the-ground surveys—especially where pinpoint accuracy is required or where surveying extends to subterranean features.
For inspectors, satellite data can be instrumental in ensuring that construction activities abide by environmental and regulatory requirements. Inspectors can use the data to validate that the physical infrastructure aligns seamlessly with approved designs. Furthermore, in the event of inappropriate or illegal practices, like unauthorized waste disposal or unauthorized construction sprawls, satellite images provide clear evidence.
Lastly, for owners, satellite data provides a panoramic and comprehensive view of their assets. From a macro lens helping to monitor progress during the initial planning and construction phases to a meticulous tool for ongoing facility management, owners can monitor structural health, coordinate maintenance schedules, and even gauge potential threats from natural disasters.
In essence, when it comes to high-level data collection over a vast geographical area like a construction mega project, satellites are the only way to map the entire site. The technology facilitates informed decision-making and transparency throughout the construction lifecycle, ensuring all stakeholders are both well informed and also held accountable. It streamlines coordination, enhances efficiency and precision, and ultimately leads to more successful outcomes for everyone involved.
A future of enhanced stakeholder confidence
The world of construction is fraught with challenges, but the integration of satellite data is poised to be a game-changer, particularly for the management of expansive mega projects. It offers unparalleled situational awareness, facilitating informed decision-making and risk management across all phases of the construction lifecycle. Every stakeholder, from property developers to environmental inspectors, can harness its potential: beginning with the careful tasks of site selection and project design, through the strategic orchestration of activities and compliance monitoring, right up to and including long-term facility management.
With satellite data in their toolkits, construction companies can benefit from enhanced project management, better quality control, and improved safety—all of which translates into successful projects delivered on time and within budget. In the final segment of our series, we will delve deeper into precisely how this is done, by considering which construction KPIs can be measured using satellite data.
Did you like the article? Read more and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!