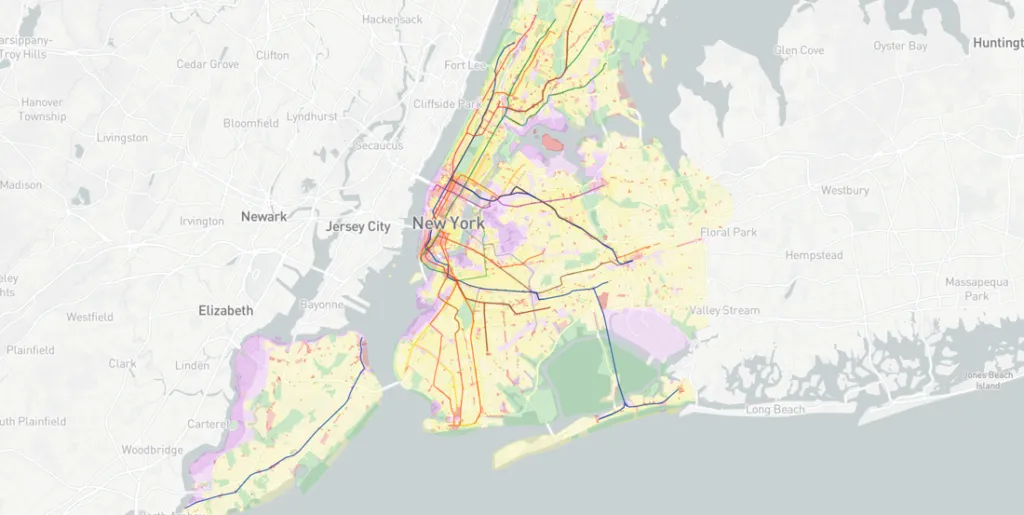
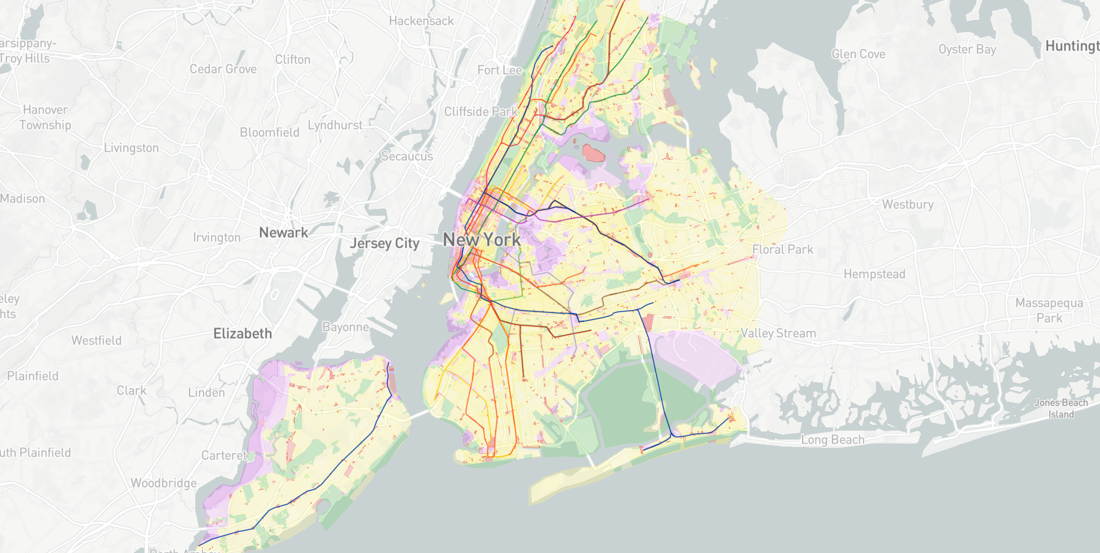
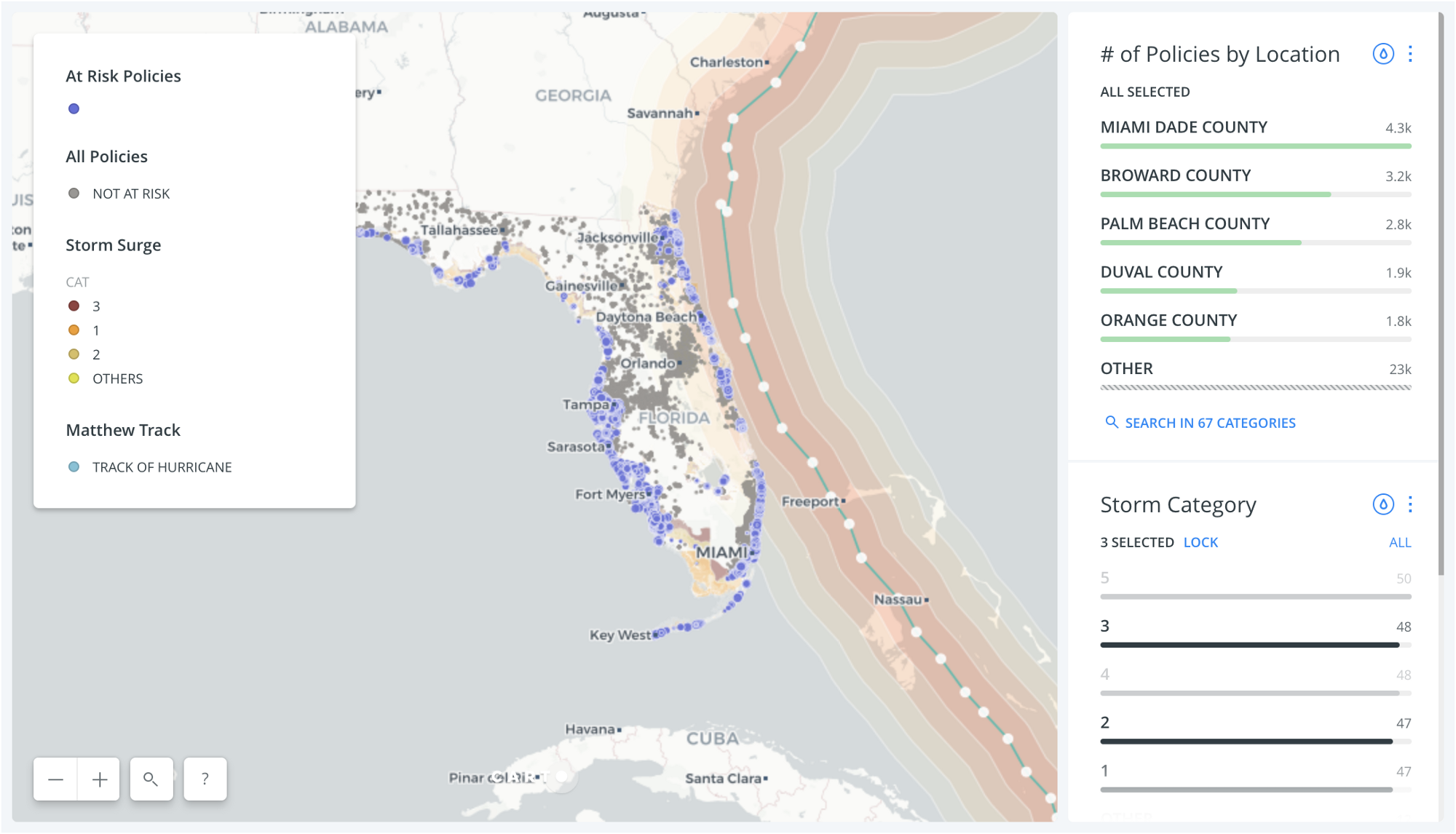
Looking into GeoSpatial 2018. Industry trends according to Joe Francica, MD of Location Intelligence Solutions, Pitney Bowes
 As we enter 2018, geospatial technology is adapting to a changing business climate where there is a heightened awareness of its value. Geospatial technology has evolved from web mapping (think Google Maps) and car navigation (think in-vehicle systems) to embedded geoprocessing for Hadoop and advanced visualizations for business intelligence solutions. Here are a few things to consider:
As we enter 2018, geospatial technology is adapting to a changing business climate where there is a heightened awareness of its value. Geospatial technology has evolved from web mapping (think Google Maps) and car navigation (think in-vehicle systems) to embedded geoprocessing for Hadoop and advanced visualizations for business intelligence solutions. Here are a few things to consider:
Big data is just data. However, there are solutions now that can process the volume and speed of information more efficiently. Significantly, though, location continues to bring essential context and the capability to calculate more data, and hence, more answers to geospatial questions can be facilitated. Questions, that before seemed impossible to consider because of the myriad attributes required to deliver an answer, are now possible to pose. Spatial calculations and spatial statistical models that benefit from crunching more data is facilitated by utilizing big data frameworks.
Security and geospatial. Whether it is a natural disaster, terrorist activity or cyber-threat…every incident happens somewhere. Acquiring numerous sources of location-based data will provide the foundation in mitigating threats to personal, economic and national security. With the aforementioned big data frameworks, connecting the electronic dots that may reveal the complex web of security threats becomes more feasible.
Geospatial precision. Collecting geospatial data with high precision is driving many new applications. Our IT infrastructure (e.g. big data frameworks; computer clusters) has allowed new applications to be realized because it was believed to be too costly previously. For indoor location applications where mobile trace data is available, as well as remotely sensed, Earth observation (EO) imagery, where higher spatial resolution is regularly captured, time to value is shorter. Machine learning is accelerating spatial data processing. Resource mapping and change detection that requires EO data is faster and therefore higher resolution data with more pixels to process is no longer an impediment.
Economic value of GIS. It is important to recognize the value of geospatial technology but it is hard to quantify. Intrinsically, we understand the importance of visual discovery through mapping. However, how does that translate into dollars and cents? By one measure, documented by consultants in Australia, the value may be between .5% and 1% of a country’s gross domestic product. Apply that value range to a city, and it’s easy to calculate the payback period for investing in geospatial software and data.
New nomenclature. It is hard to get accustomed to new ways to discuss information processing. Machine learning is a good example. Supervised classification, a common method of creating thematic maps from EO imagery is, according to Wikipedia, is a subset of Machine Learning. So, historically, many remote sensing geospatial scientists have been using Machine Learning since digital imagery has been around. Now we need to talk about it differently.
And finally, there are AI devices like Siri and Alexa. We are now seeing how voice recognition technology is capable of taking a simple semantic statement, processing each word, providing context and then returning a result to the user. If we asked Siri a geospatial question, what kind of answer would you get? Take this question: Hey Siri, find me all of the class A commercial real estate parcels that are available for lease near the intersection 4th Avenue and Main Street in Happy Town, UK and extending outward for 5km. How would Siri respond? Would it show you a map? Or just a listing of properties? Ideally, you’d like both and perhaps it would calculate the Net Present Value of each property’s cash flow for 10 years. Now, that’s AI!
In summary: forecast CAGR of 34% to 2025
Evidence that the wider market is becoming more aware of the value of geospatial can be seen in ‘Location of Things’ forecasts from business intelligence company Research and Markets1. The market will be worth $71.6 billion by 2025, they say, and is growing at a CAGR of over 34%.
Businesses are seeing value in connecting data relating to people, places and things: it uncovers invaluable insight which improves decision making, facilitates a deeper understanding of customers, and enhances customer engagement. Here at Pitney Bowes, we call this understanding of the relationship between people, places and things the Knowledge Fabric, as data is woven together to uncover hidden knowledge and expertise.
2018 will be the year geospatial accelerates, the opportunities become more diverse and the understanding of its value deepens.
1,2 Study from Research and Markets cited in The Drum