Integration Of Car And Smartphone? ‘Automatic Link’ Connects Your iPhone To Your Car
 The Automatic Link is a new iPhone accessory that connects to the OBD (on-board diagnostic) port which is installed in every car but is usually used only by mechanics. Every car has a sort of computer (more or less advanced) that produces live data about the vehicle’s speed, fuel level, error reports etc. however drivers have a very limited access to this information. Now imagine what will happen when you integrate this data with location-aware smartphones… Do you already get the point?
The Automatic Link is a new iPhone accessory that connects to the OBD (on-board diagnostic) port which is installed in every car but is usually used only by mechanics. Every car has a sort of computer (more or less advanced) that produces live data about the vehicle’s speed, fuel level, error reports etc. however drivers have a very limited access to this information. Now imagine what will happen when you integrate this data with location-aware smartphones… Do you already get the point?
How it works?
Essentially Automatic Link is a small device which you plug-in to the OBD port and it connects to your iPhone (Android coming soon) via Bluetooth 4.0. Once linked, it will launch Automatic app on the smartphone and give you access to a lot of cool data and features.
What it does?
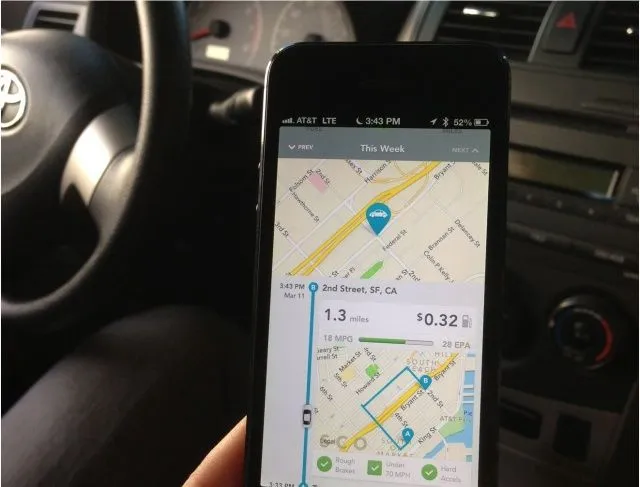
Automatic has a lot of cool features. It’ll monitor and analyse your driving habits and routes in order to help you be more fuel-efficient. It will generate a trip report for every journey with a map that shows exactly where your car went, how much gas was used, and how much did it cost you. It will give you weekly trends, compare different styles of different drivers of the same car and much more…
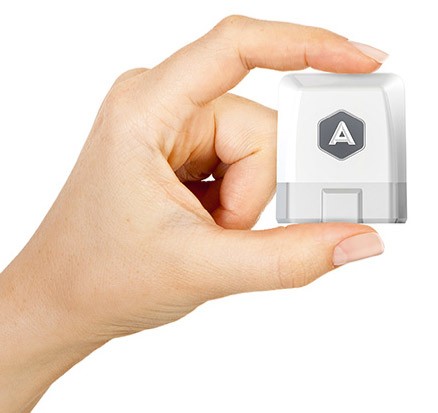 Automatic will dial 911 and alert your relatives if you get in an accident. Moreover it will give you access to full diagnostic reports of your car, so that you don’t need to go to garage every time a warning indicator lights up. But there as well some other cool features like parking place reminder and so on.
Automatic will dial 911 and alert your relatives if you get in an accident. Moreover it will give you access to full diagnostic reports of your car, so that you don’t need to go to garage every time a warning indicator lights up. But there as well some other cool features like parking place reminder and so on.
Limitations and verdict
Of course there are always some limitations. First of all it will be available only in US (for now), secondly it will not support diesel cars for now. Moreover there will be no API for developers to make even cooler stuff with it. Automatic will be available for pre-orders from May for around $70 and I think it’s worth every penny. It gives you access to data about you car and your driving behaviours and adds location dimension to this equation. Can you think about anything cooler?