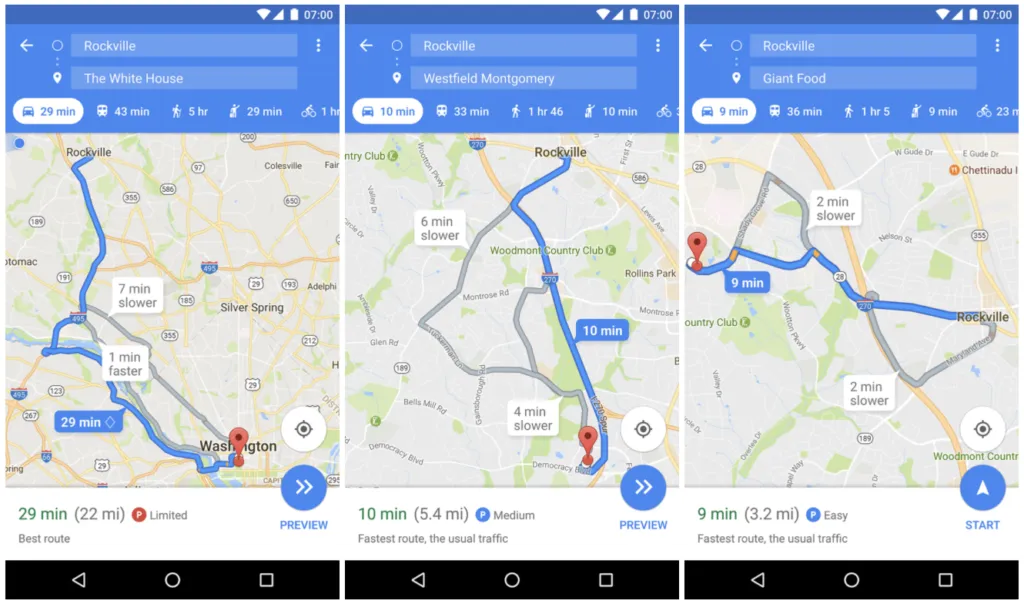
Google Maps will be soon showing parking availability data
It is estimated that even up to 30% of traffic on some streets may be related to searching for a parking spot. It often happens that driving to a city center takes you less time than cruising around searching a place to leave your car, and therefore parking information is the next big thing in the navigation industry.
Unfortunately, it is a very complex issue. Every serious mapping company in the world is looking into this problem from at least a couple of years without any spectacular results. To solve it, first of all, you need to map each and every parking spot in the city. Then you need to know which one is free. The optimal option would be to put a sensor below or above each spot. In this scenario, there is a question who will pay for and maintain it. Some cities are piloting that sort of solutions but today it is still too fragmented and not standardized to use it on a large-scale.
Another solution comes with connected car sensors. Almost every new car has built-in cameras or parking proximity sensors. Data from these sensors could be used to detect free parking spots. Unfortunately, in practice it is much more difficult than it sounds. First of all the number of connects cars is still too low. Secondly, it could only work if data from many different car brands would be shared and used together which today is still difficult to image.
Finally, there is a third solution and Google is piloting it. For some cities in the US, the company has measured the number of free parking spots (most likely based on Street View) and now it is using probe data (the same data which is used to estimate traffic) to assess what is the probability of finding a free parking place in the area.
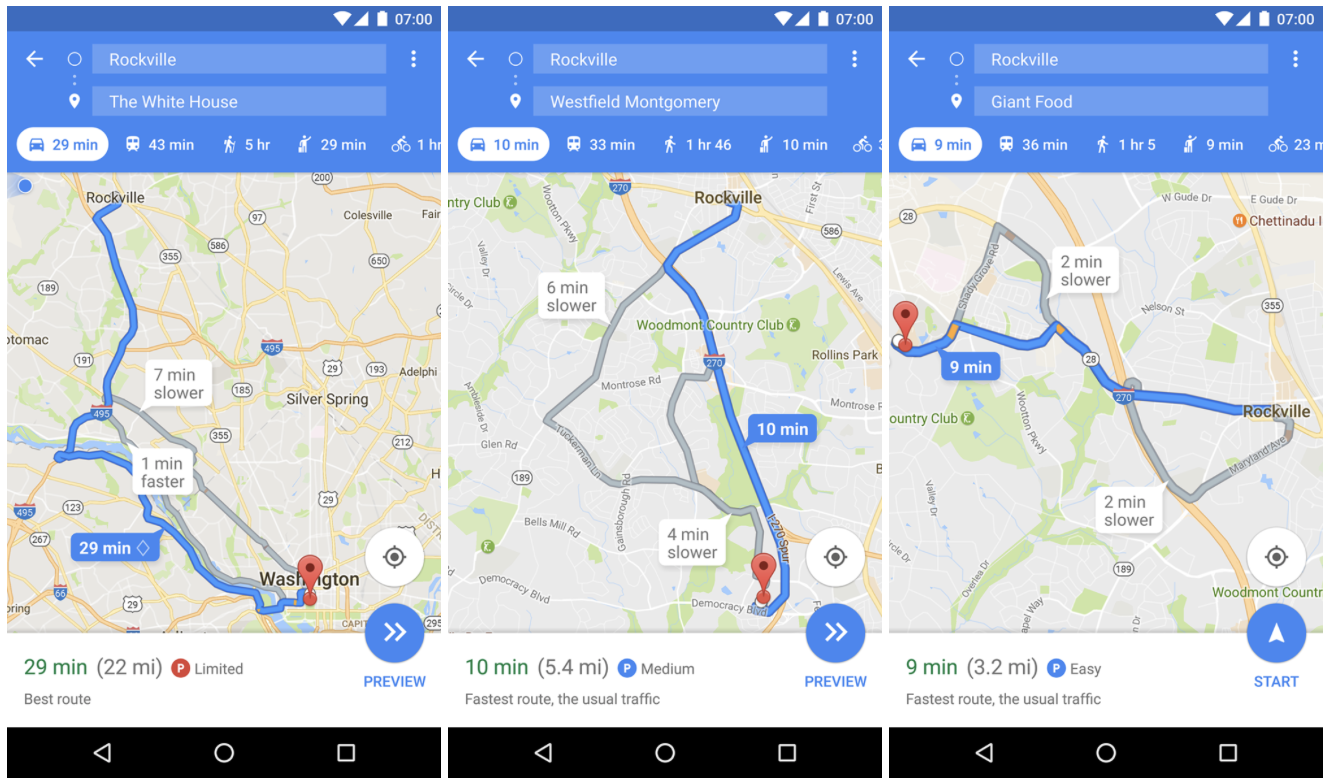
The information is displayed as a small rounded P icon next to your estimated travel time when you search for driving directions. The information is then followed by a text description. There are three levels of parking availability probability: Limited, Medium, and Easy. The accuracy of the estimations is hard to assess for users but Google can do it very accurately and calibrate the feature depending on location. When you reach the destination you have selected in the app, the company can measure how long does it take you to get out of your car. This means that the estimations should get more accurate with time.
The feature has been rolled out in a couple of cities in the US to Android users that subscribed to Google Maps beta program. It again proves that Google is a undisputable leader in the navigation industry.