Exploring New Geospatial Features on Google Maps
Google Maps has long been a leader in digital navigation, offering directions and location insights to users worldwide. In 2023, Google introduced several new features that use geospatial technology and artificial intelligence to improve user experience. These updates not only support existing services but also introduce new abilities that promise to change how we interact with our environment.
Immersive View for Routes
One of the most notable introductions is the Immersive View for Routes. Developed in major cities, this feature allows users to visualize their entire journey in a dynamic, three-dimensional space. By combining AI with extensive Street View and aerial photography data, Google Maps can now provide a detailed, photorealistic preview of travel routes.
This 3D visualization is particularly useful for planning as it includes real-time elements like traffic conditions and weather forecasts. Users can simulate different departure times to see how conditions change, making it easier to plan trips efficiently. For cyclists and pedestrians, this feature enhances safety by allowing them to familiarize themselves with the route details, such as turns and landmarks, before heading out.
Immersive View, Dublin

Immersive View for Routes, Dublin
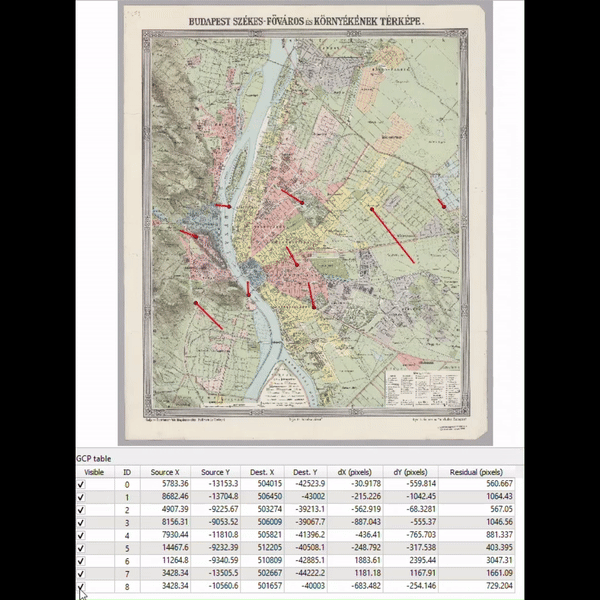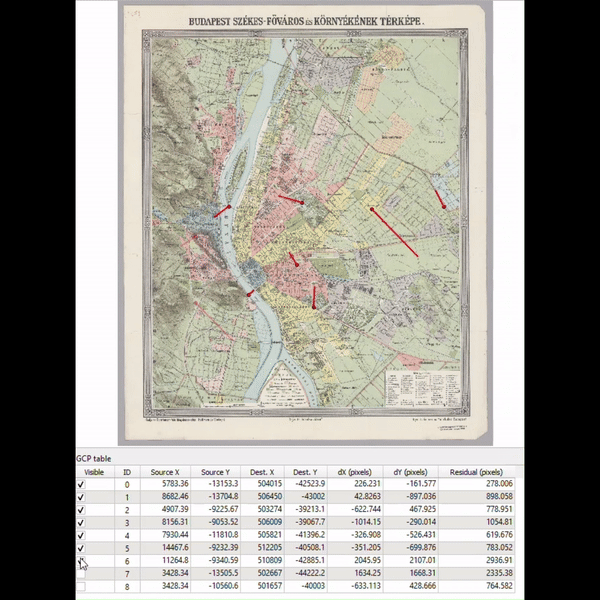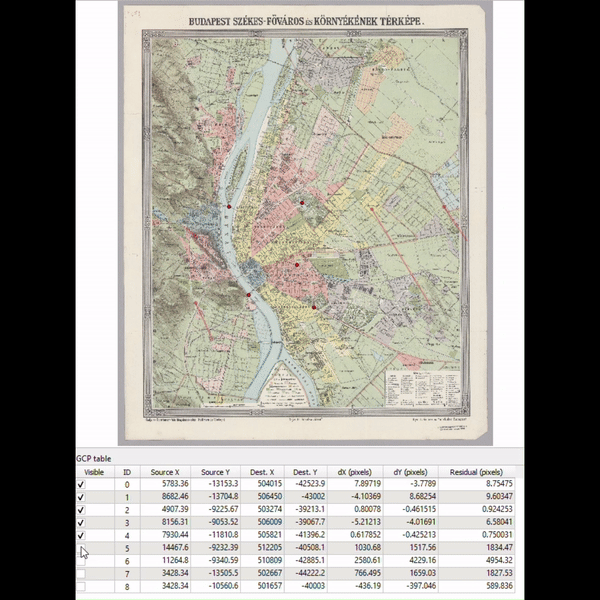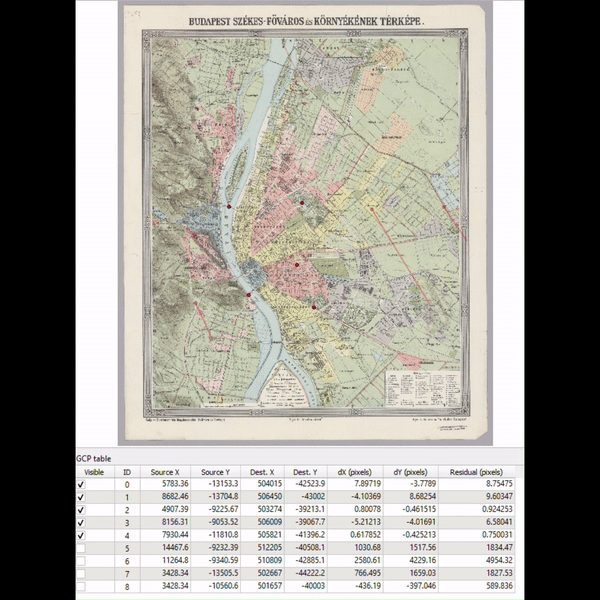
Google Maps’ Immersive View for routes transforms navigation by stitching together billions of high-resolution images from aerial surveys and Street View captures. The photogrammetric technique aligns these images with existing map data, creating a precise digital visual.
AI and machine learning then label critical route details like street signs and building entrances from these images. The transformation from 2D to 3D is achieved using multi-perspective aerial cameras, which accurately model terrain and building heights. This detailed 3D map allows for dynamic route visualization with camera movements that show both overarching route plans and close-up navigational tips. Real-time data overlays such as traffic conditions and weather are added, enhancing route planning. This integration of detailed visuals and real-time information is now enhancing navigational confidence for users in cities like Amsterdam, Dublin, New York, and Tokyo.

Immersive View for Routes, Dublin

Fusion of StreetView and Immersive View, Los Angeles
AR Possibilities with Lens in Maps
Lens in Maps, formerly known as Search with Live View, has expanded its functionality. Now available in over 50 new cities, this feature utilizes augmented reality and AI to help users quickly orient themselves in unfamiliar surroundings. By simply pointing their smartphone cameras, users can get real-time information about nearby places like restaurants, ATMs, and public transport stations. This instant data layer helps users navigate spaces more confidently and efficiently.
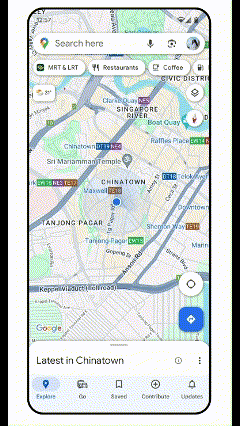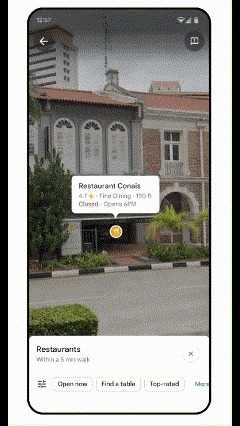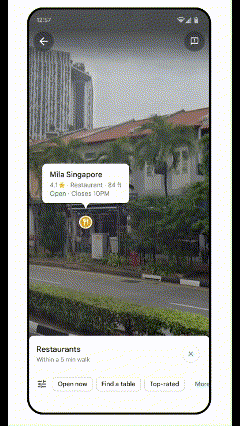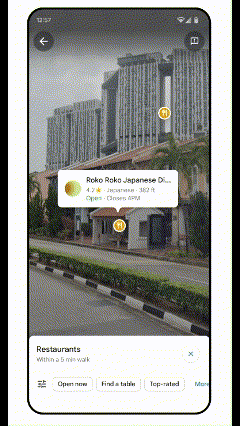
AR Lens, Tokio
Photorealistic 3D Tiles in Google Maps Platform
The launch of Photorealistic 3D Tiles marks a significant advancement in Google Maps’ possibilities. These tiles allow developers to create more engaging map experiences. For instance, real estate companies can use these tiles to show potential buyers detailed 3D models of properties and their surroundings, enhancing the buying experience by providing a more comprehensive view of the area.

Source: 3d-tiles.web.app
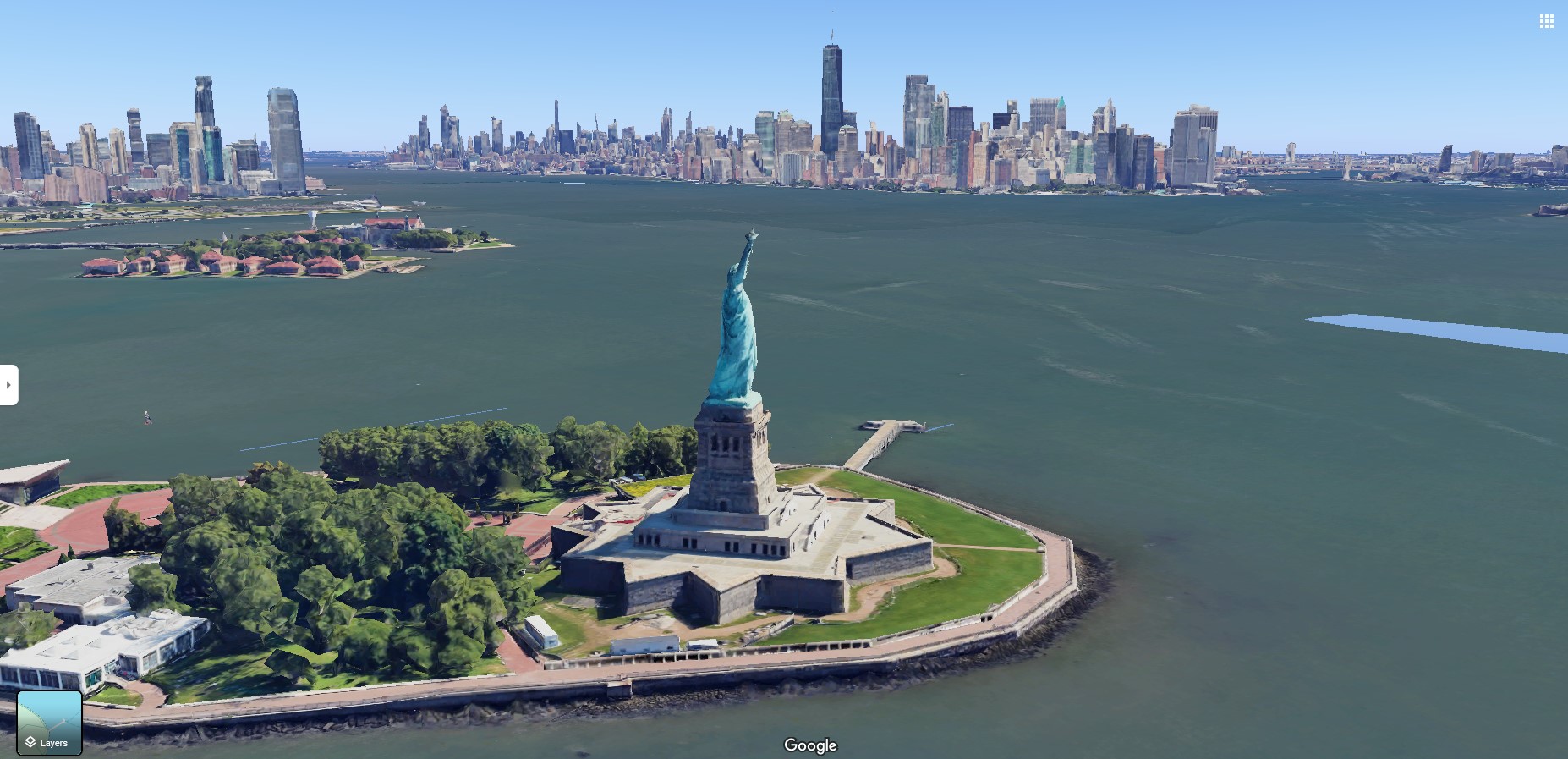

Example of 3D Tiles, New York
Example: The Importance of Vegetation in Prague, Czech Republic
Prague’s use of Google Maps’ 3D Tiles to study urban vegetation showcases the practical applications of these advanced geospatial tools. By analyzing 3D models of the city enhanced with data on existing vegetation, planners can assess the impact of green spaces on urban heat islands, air quality, and biodiversity. Such insights have a huge impact on developing strategies to integrate more green areas into urban planning, which can lead to healthier, more sustainable city environments.
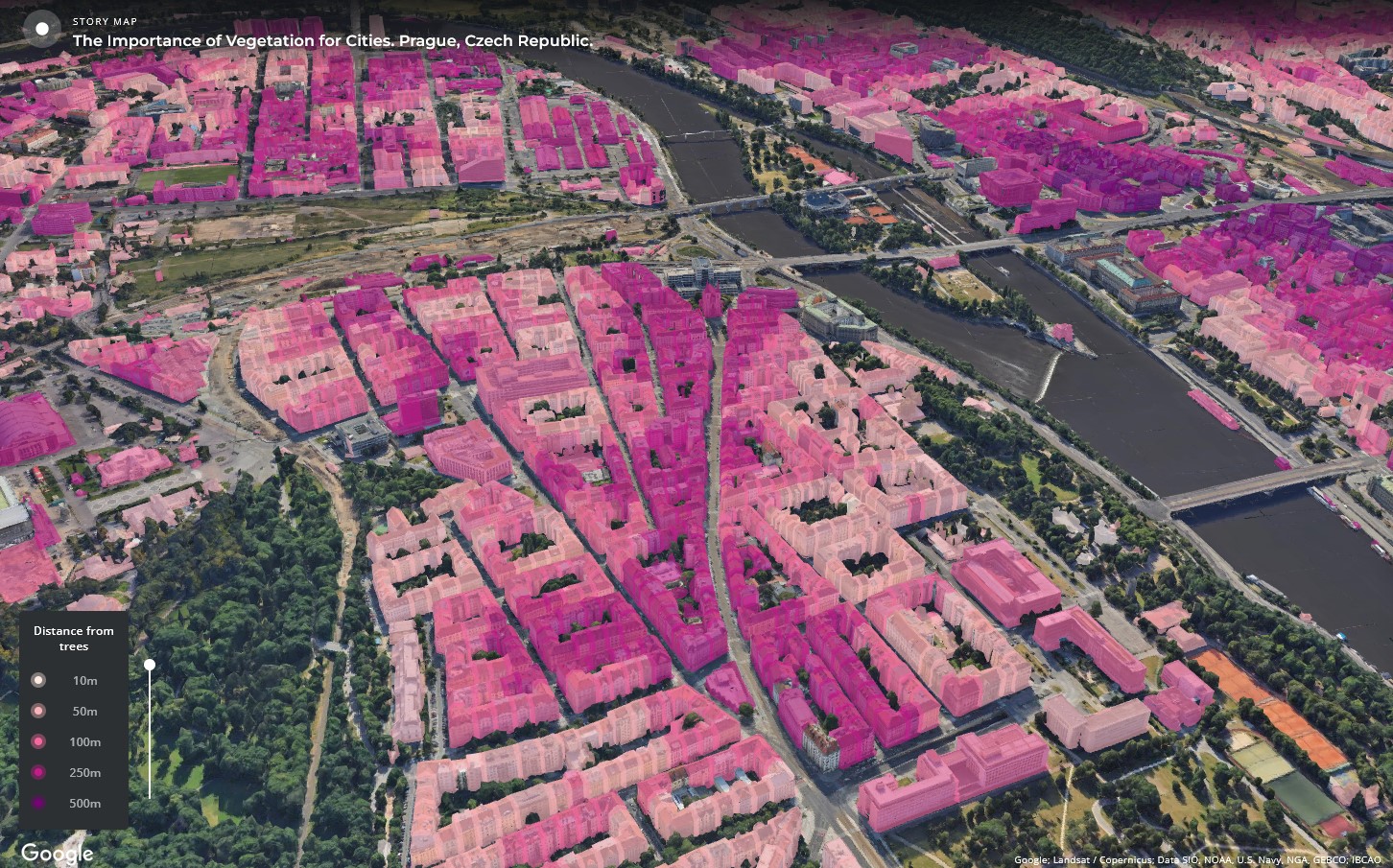

3D Tiles, Prague
Check out this project here: carto.com
Future Directions of Google Maps Features
These updates from Google Maps highlight the growing importance of geospatial technology in everyday applications. Google Maps continues to set the standard for digital mapping and navigation. Its latest updates, not only improve how we view and interact with our immediate environment but also offer tools that can help shape the future of urban landscapes worldwide. By integrating AI and 3D visualization, Google Maps is enabling more informed interaction with the places we live and visit.
Did you like this post? Read more and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!