The Revolution of True Orthophotos: Precision in Urban Planning, Construction, and Environmental Monitoring
Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, true orthophotos have emerged as indispensable tools, transforming how we visualize and analyze the Earth’s surface. Orthophotos have become integral products in various industries, from urban planning to environmental monitoring.
While traditional aerial photos have long been valuable, they often fall short in terms of accuracy due to distortions caused by topographic relief, lens distortion, and camera tilt.
True orthophotos, on the other hand, provide a distortion-free, accurate map-like view of the Earth’s surface. This article explains the technology behind true orthophotos, their advantages over traditional aerial images, and their applications in various fields.
What Are True Orthophotos?
A true orthophoto is an aerial image that has been geometrically corrected (orthorectified) to remove distortions caused by the camera angle and terrain.
This is a view of a given object from a perspective located at an infinite distance from the given object of interest – best shown in the illustration below. The farther from the ground surface, the smaller the distortions. For this reason, high-resolution photos from the satellite ceiling are becoming increasingly popular in creating true orthophotos.
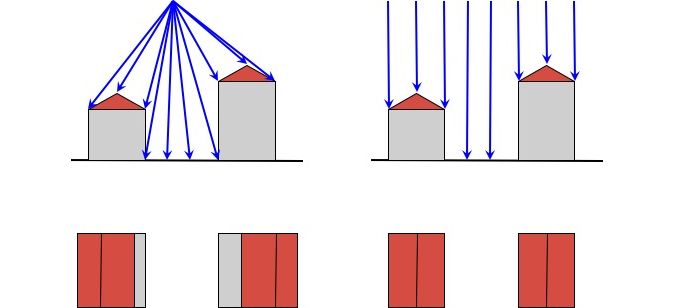
Traditional orthophotos vs. true orthophotos. Source: GIM International
This correction process ensures that the scale of the photograph is uniform, making the true orthophoto an accurate representation of the Earth’s surface, akin to a map.
True orthophotos represent a significant advancement, offering a uniform scale and accurate representation of the Earth’s surface. Unlike traditional orthophotos, true orthophotos account for the three-dimensional shape of the terrain and objects, ensuring that all elements are in their correct horizontal positions.
In traditional orthophotos, shifts of elements protruding above the ground surface, e.g. building roofs, are often visible.
The Technology Behind True Orthophotos
Case study: Keitschick Homestead, Kluki, Poland
To illustrate the process of creating true orthophotos, let’s examine a case study of a historic cottage named Keitschick Homestead from the Slovinian village museum in Kluki, Poland
Creating a true orthophoto involves several steps:
- Image Collection:
- High-resolution images are captured using UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) or aircraft equipped with specialized cameras.
- These images are taken at various angles to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- Case study: 122 images of the historic cottage were taken
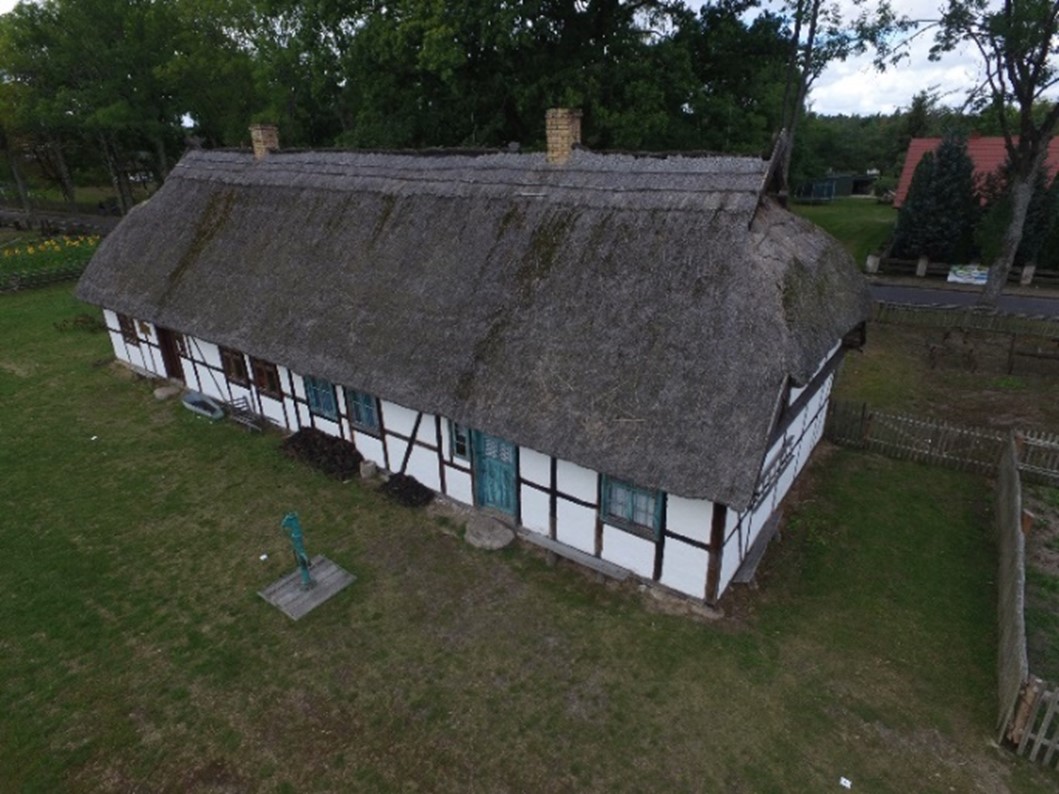

Case study, one of 122 images of a historic cottage, in Poland
- Digital Surface Model (DSM) Creation:
- A DSM is generated from the collected images using photogrammetric techniques.
- This model includes the elevations of terrain and above-ground features like buildings and trees.
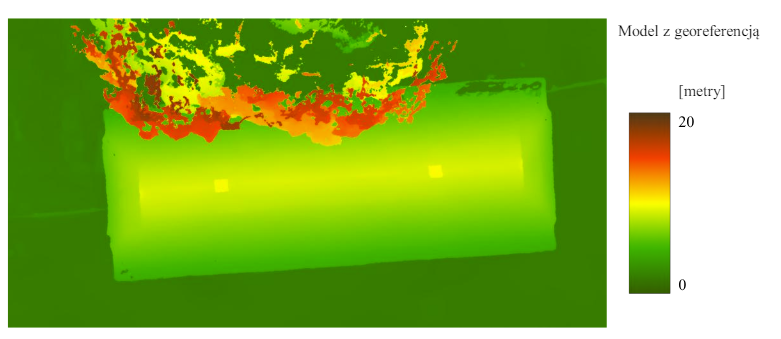
Case study, DSM model
- Orthorectification:
- The DSM is used to orthorectify the images, correcting for distortions and ensuring that all objects are correctly positioned.
- This process involves algorithms that adjust each pixel based on its elevation and position.
- To verify the accuracy of orthophoto and to add georeferencing to the photogrammetric model, the photogrammers use Ground Control Points (GCPs).
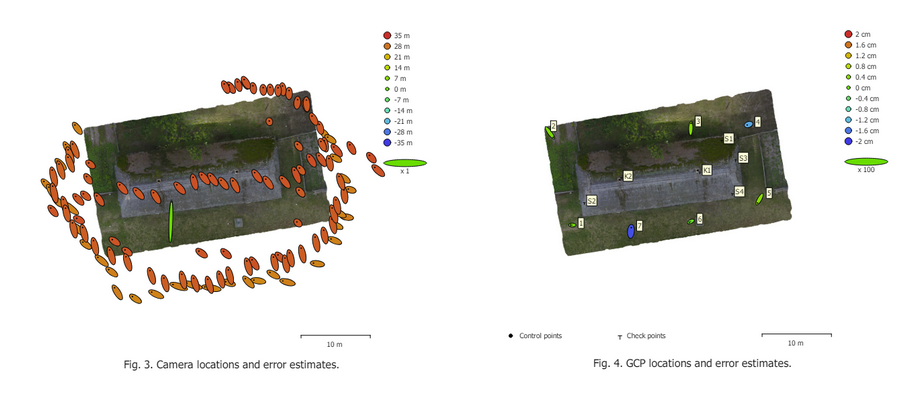
Case-study, camera and Ground Control Points error estimates
- Mosaicking:
- The corrected images are then stitched together to create a seamless orthomosaic.
- Photogrammetric softwares ensure that the overlaps are handled smoothly, and any discrepancies are minimized.
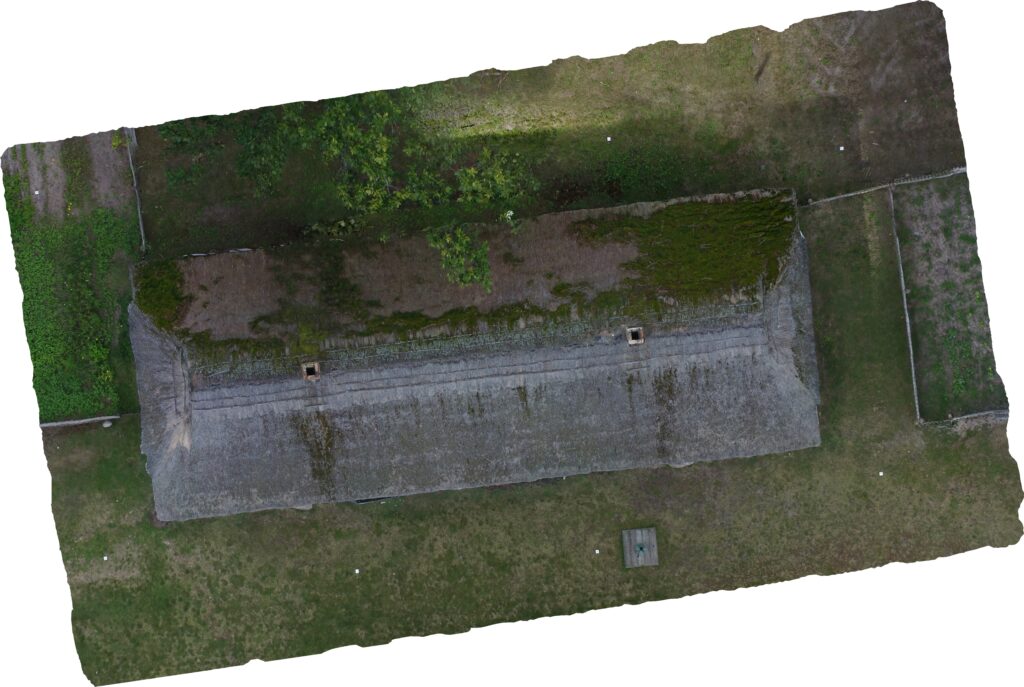

Case-study, final product
For examples of high-quality orthophotos and orthomosaics, visit Maps Made Easy, which showcases impressive samples of these technologies in action.
- Additional products:
- Orthoelevations are a product of photogrammetric processing.
- They can be used as a texture in rendering 3D buildings in virtual reality or simply in conservation.
- The idea is similar while producing true orthophotos, but in this case, the observer stands at an infinite distance from the facade of the building.
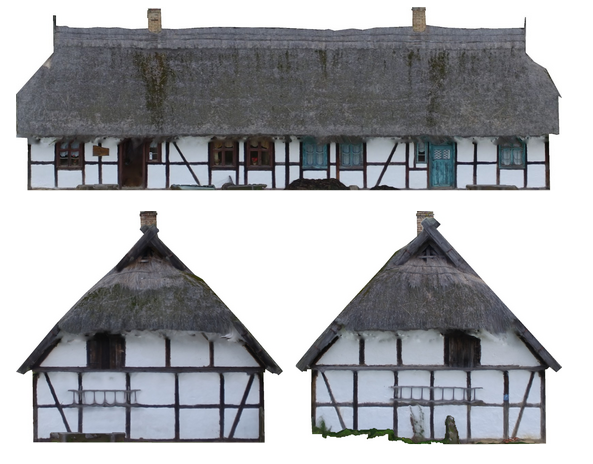

Case-study, orthoelevations
Advantages of True Orthophotos
True orthophotos offer several advantages over traditional aerial images:
- Accuracy: True orthophotos provide a highly accurate representation of the Earth’s surface, with a positional accuracy of less than a meter or even several centimeters. This accuracy is crucial for applications that require precise measurements and analysis.
- No Distortion: Unlike traditional orthophotos, true orthophotos do not exhibit distortion from building lean or terrain variations. Every feature is shown from a direct top-down perspective, ensuring consistency and reliability.
- Enhanced Detail: True orthophotos capture fine details such as individual buildings, trees, and other features, making them invaluable for urban planning and detailed land use analysis.
- Consistency: These orthophotos maintain consistency across different datasets, making them ideal for change detection and monitoring over time.
Applications of True Orthophotos
Urban Planning
True orthophotos are useful in urban planning. They provide city planners with precise, up-to-date imagery that can be used to map out new developments, assess infrastructure, and analyze population trends. The accuracy and detail of true orthophotos ensure that planning decisions are based on reliable data.
Construction
In the construction industry, true orthophotos are used to monitor project progress, plan site layouts, and ensure compliance with design specifications. The ability to measure distances and areas accurately from orthophotos helps in resource management and project planning.
Environmental Monitoring
True orthophotos are essential for environmental monitoring. They allow for the detailed observation of changes in vegetation, water bodies, and land use. Environmental scientists use these images to track the effects of natural disasters, human activities, and climate change, facilitating informed decision-making for conservation efforts.
Challenges and Best Practices
While the creation of true orthophotos is straightforward in theory, it involves several challenges:
- Image Overlap: Ensuring sufficient overlap between images is critical. Without proper overlap, gaps and inaccuracies can occur. A general rule is to aim for at least 70% overlap.
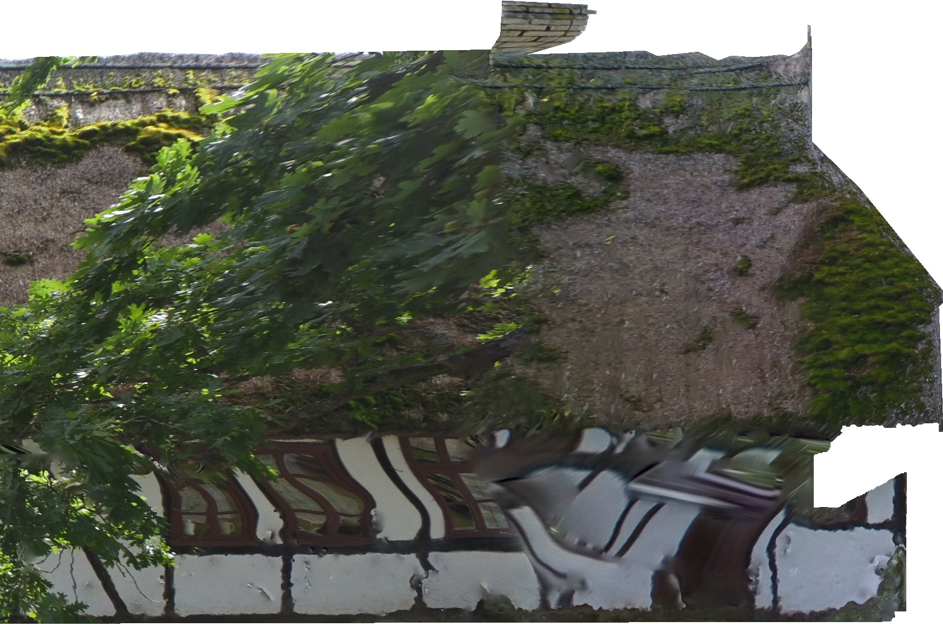

Case-study, the effect of low image overleap may lead to distortions of the final product
2. Lighting and Camera Settings: The quality of images can be affected by lighting conditions, camera settings, and weather. Overcast conditions generally provide the best results, as they minimize shadows and glare.
3. Flight Planning: A well-planned flight path is essential to capture consistent, high-quality images. Adjustments for altitude and speed need to be made to account for varying terrain heights and to avoid blurry images.
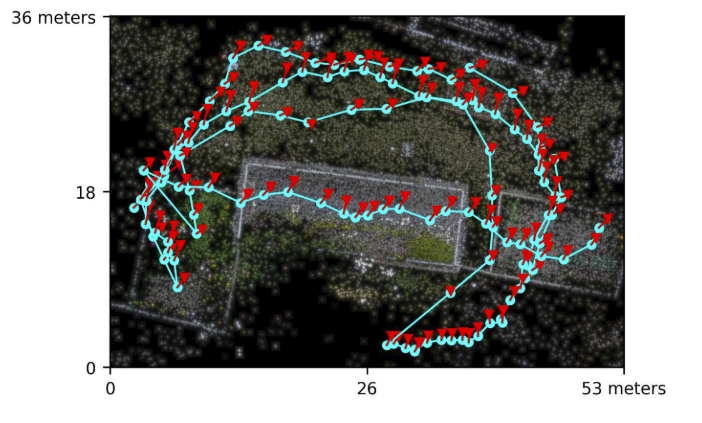
Case-study, post-flight path
Choosing the Right Software
The choice of software for processing orthomosaic maps is crucial. Here are some key considerations:
- Processing Speed: Cloud-based solutions like WebODM often provide faster processing times compared to on-premises software, especially when handling large datasets. This software may process all collected data much faster than manual processing. However, cloud processing may sacrifice some control over the process so the user is not fully protected against the detection of big errors.
- Accuracy: Look for software that offers tools for ground control points and scale constraints to enhance the final product’s accuracy. Correlator3D and Pix4D Mapper tend to produce highly accurate results.
- Stability: Ensure the platform is reliable and capable of handling large projects without crashing or errors. Cloud-based solutions often provide better stability.
- Ease of use: User-friendly interface can significantly reduce the learning curve and streamline workflows. WebODM is relatively easy to use once set up, while Correlator3D offers automated templates.
Summary
True orthophotos represent a significant advancement in the field of aerial imaging. Their accuracy, lack of distortion, and high level of detail make them invaluable tools in various industries, including urban planning, construction, and environmental monitoring.
By leveraging advanced technologies and following best practices, true orthophotos provide precise, reliable data that supports informed decision-making.
For those interested in exploring the capabilities of true orthophotos, Maps Made Easy offers excellent examples and resources to get started. As technology continues to evolve, the applications and accuracy of true orthophotos will only improve, further solidifying their role as essential tools in modern geospatial analysis.
More about ortho imagery you can find in our article: What is the difference between orthophotos, orthophotomaps, orthomosaics and true orthophotos?.
Did you like the article? Read more and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!