How to predict covid19 impact on urban retail.
How to predict covid19 impact on urban retail. A geospatial risk evaluation model.
As soon as the covid19 crisis broke out, lockdown forced retail stores to close in order to avoid contagion. EIXOS started developing a geospatial model to predict the economic impact on urban retail. In parallel, an MIT research team published a proposal for a predictive model. MIT model assesses risk factors complementary to those assessed by EIXOS.
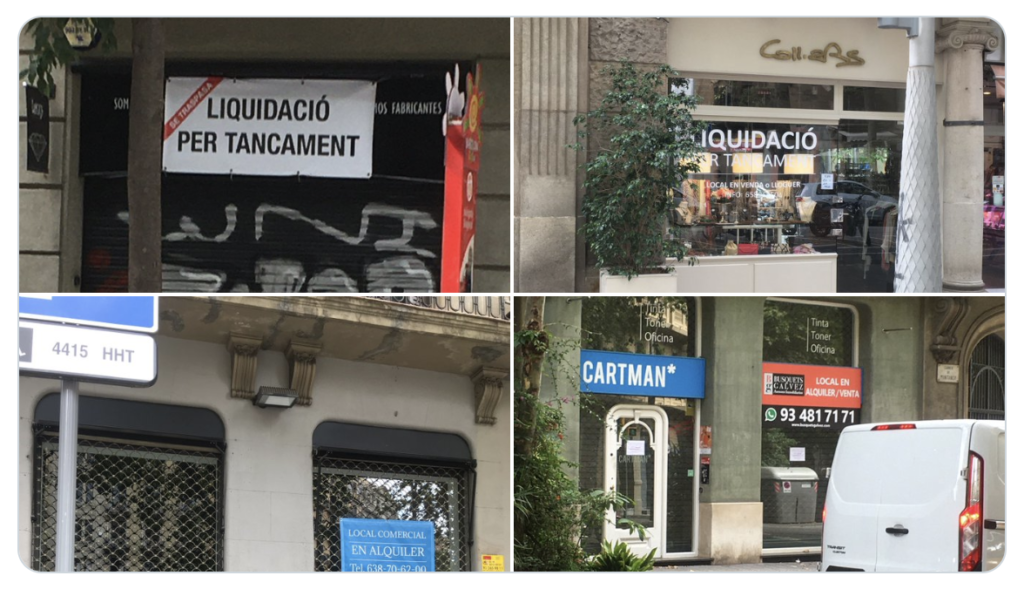

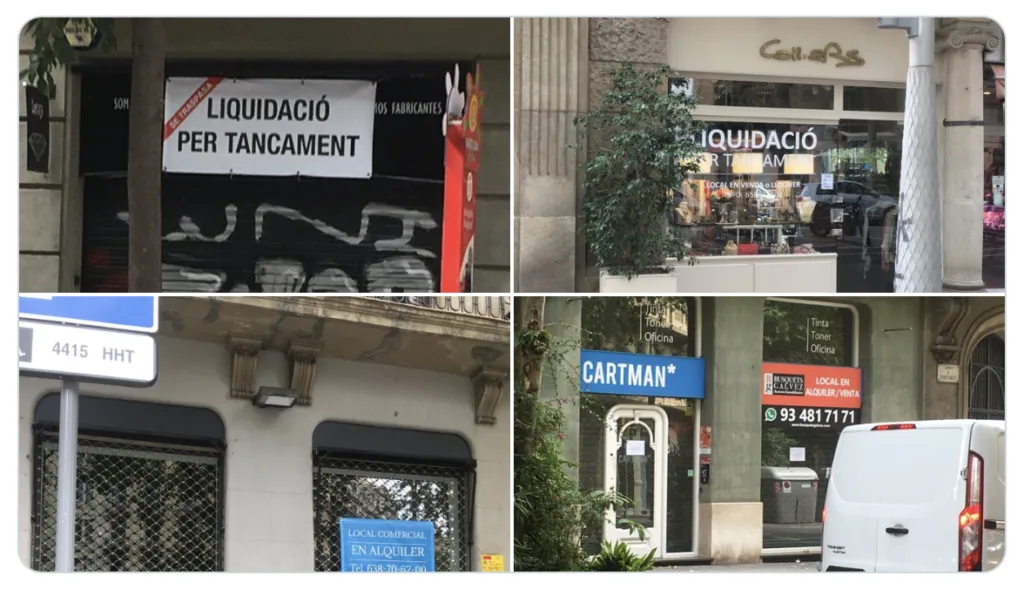
Barcelona: business that were open in March 2020 are now definitely closed as a consequence of covid 19 lockdown. Photographer: @gasgerm161 (twitter)
On 2nd April we released a predictive model that we applied in Barcelona first and in New York later.
On 24th April, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology research team formed by Seth G. Benzell, Avinash Collis, and Christos Nicolaides published an article in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS). They also propose a risk model for calculating the impact on small business.
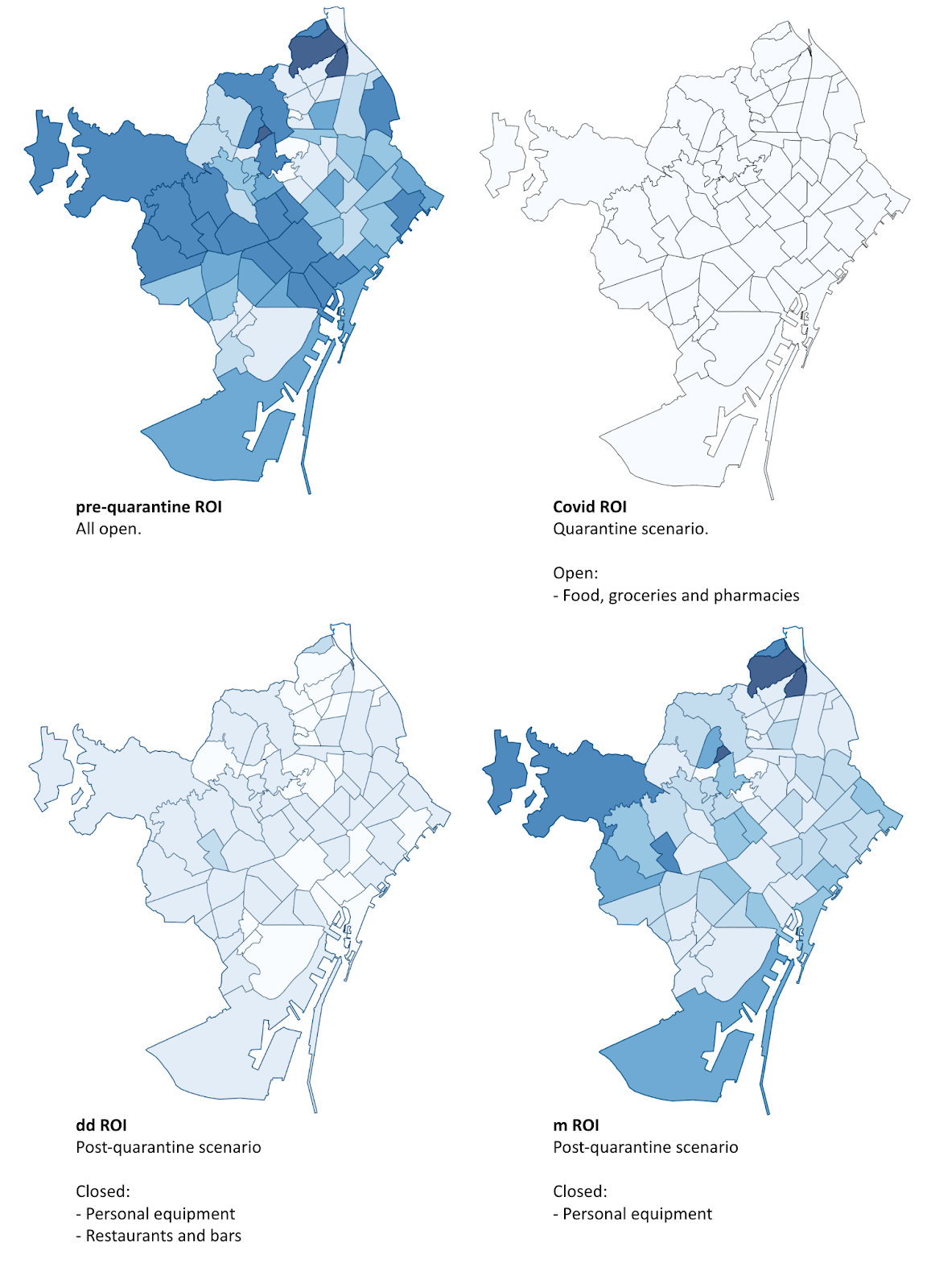
EIXOS geospatial covid19 impact on urban retail risk model
It is based on data on the retail composition of entire cities. These cities were mapped by the EIXOS international geographical network.
The model evaluates the risk of excessive financial stress caused by covid19 lockdown, that could lead to business closure.
We measure the risk activity by activity, taking into account several factors:
– Whether or not it is essential in terms of lockdown, according to authorities.
– If it is labor intensive, which adds financial stress.
– If it stores expiring product at the point of sale.
MIT risk model
MIT model is based data captured through user surveys. It also uses mobile phone data to measure user concentration in several types of stores.
It uses two indicators:
– user’s priority for a given sort of business, according to the preferences of the users surveyed.
– probability of infection amongst users and store staff in the normal course of business.
The (weighted) sum of these factors described in both models, EIXOS and MIT research team, gives a final potential risk for each activity.
Risk level is expressed as a percentage of business closures in a given activity (e.g., “restaurant”). It indicates the number of stores that could close as a result of covid19 impact financial stress.
Restaurant is one of the activities that adds the highest risk values. The model predicts up to 60% of restaurant closures for a full impact scenario. This means that 6 out of 10 restaurants are at risk of closure as a covid19 impact direct consequence.
The case of London, Sant Cugat, Reus and Bilbao
The resulting predictive model will be applied in London first. Sant Cugat del Vallès, Reus and Bilbao will follow immediately.
Retail recovery strategy. Opportunization.
EIXOS has spent the last few years defining new strategies for recovering and boosting urban retail.
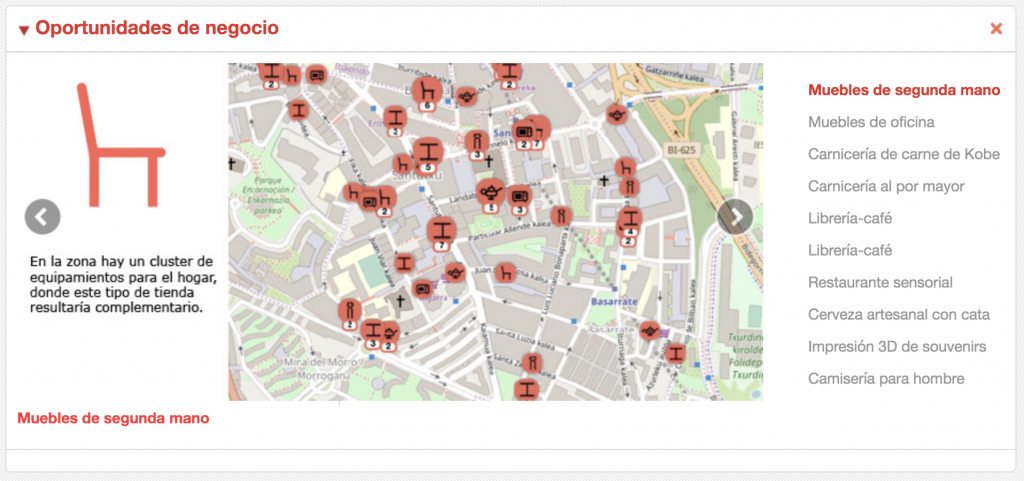
First method is the location based business opportunity detection service. It finds clear opportunities on specific locations to start a new business. Therefore, it also analyzes retail composition and availability of vacant retail spaces in order to do so. This service has been successfully deployed in several cities, such as Bilbao (Bilbaoin.com).
Second method is the so-called optimization of retail composition service. A location intelligence algorithm detects new possible combinations of retail stores in a city. Then, it proposes new configurations to improve the retail health parameters. The result is a more resilient and attractive to consumers retail scenario.
Combining both methods, opportunity detection and retail optimization, is what we call “opportunization”.
Co-authors:
David Nogué, founder & CEO at Eixos.cat
Carlos Carrasco Farré, chief data scientist & partner at Eixos
Related articles:
Covid19 Impact on Barcelona Retail
COVID-19 Impact on Manhattan Retail
Geomob video-conference: Covid19 impact on Manhattan & Barcelona
Bilbao: business location opportunity detection service.
MIT News: “Which businesses should be open?”