Precisely has emerged as a leader in address data management, with its Geo Addressing service and the PreciselyID, an elegant system in which every address is assigned a single, unique identifier. This innovation streamlines the management of address data, ensuring accuracy, consistency and reliability.
In our previous articles in this series, we explored the challenges presented by traditional addressing systems, and the advent of technological innovations like geocoding and reverse geocoding, before introducing the powerful capabilities of Geo Addressing. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the sophisticated features of Precisely’s technology and consider how the company is setting new standards in address accuracy.
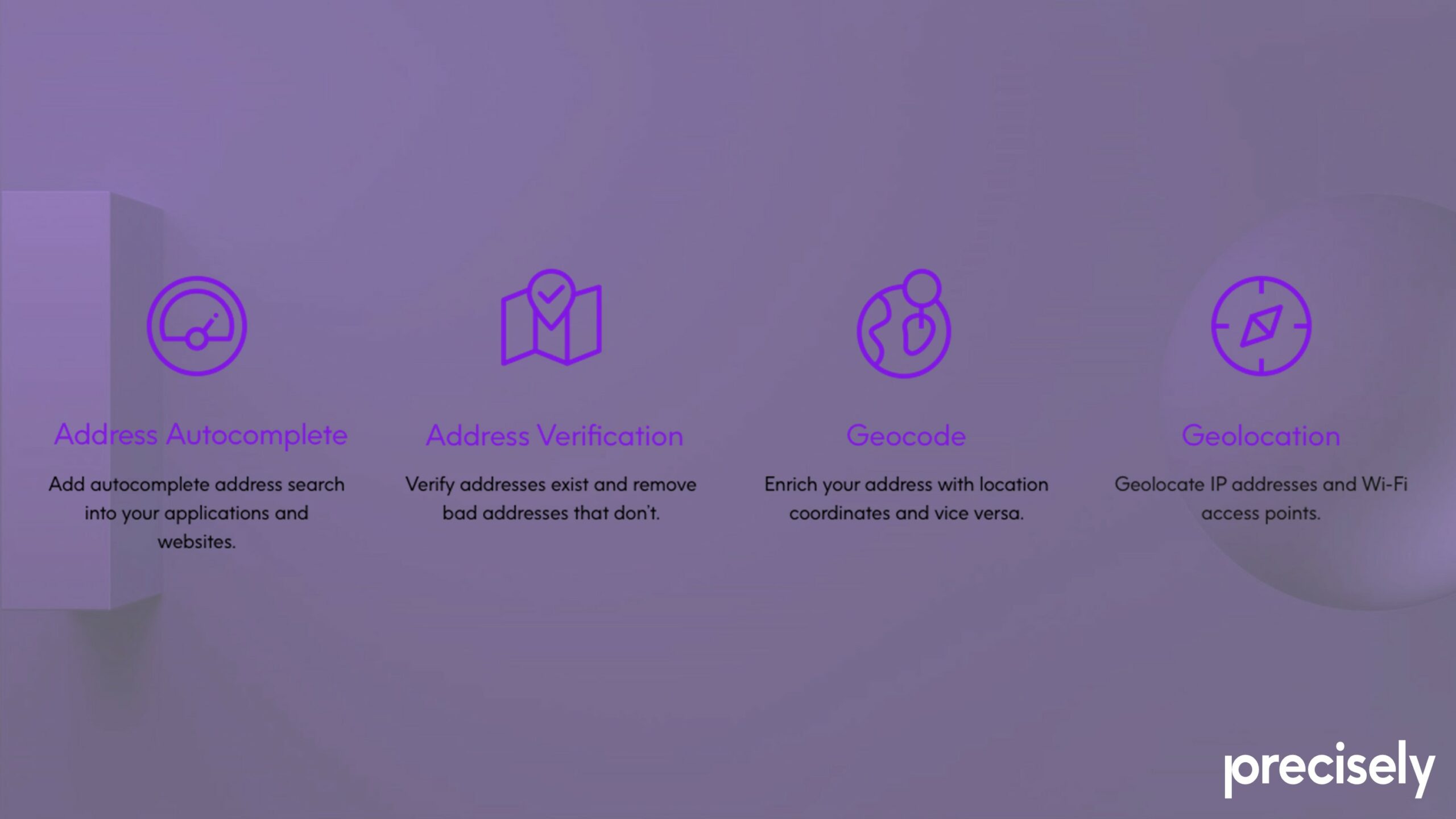
Eliminating Bad Addresses through Autocomplete, Verification and Validation, Geocoding and the PreciselyID
Bad addressing can cause a host of issues for companies. It can damage relationships with customers through late or lost delivery—as many as one in five hyper local deliveries are cancelled or late due to delivery problems—or by sending out duplicate mail from a database which has been inadequately de-duped. High rates of undelivered or returned items can also cause significant losses. And perhaps above all, bad addresses can lead to reduced operational efficiency through wasted time and resources. It is therefore essential that companies do everything they can to prevent bad addresses from entering the system. Precisely’s technology reduces instances of bad addresses through a sophisticated autocomplete system, combined with address verification and validation, geocoding—and, of course, the PreciselyID.
Read More:
Geo Addressing Decoded Part 1: Why Does Geo Addressing Matter?
Geo Addressing Decoded Part 2: Beyond Coordinates – Exploring the Depth and Impact of Geo Addressing
Geo Addressing Decoded Part 3: Diving into the Key Features of Precisely’s Geo Addressing System
Geo Addressing Decoded Part 4: Exploring the Applications of Geo Addressing Solutions
Autocomplete
Address autocomplete is effectively an intelligent form of text prediction. The software takes freeform text entered by a user, performs a search against curated reference data, and retrieves a list of relevant suggestions. The user can then pick from the list of suggestions, and the software cleans up the inputted data, eliminating bad addresses caused by human error.
Faster, more efficient and more reliable address entry also significantly reduces user frustration and abandonment, particularly in online contexts where efficiency is paramount—and in an age when attention spans are at a premium. An astonishing 4% of cart abandonment is due to problematic address entry. Autocomplete improves the user experience by minimizing the effort required to enter address details, leading to higher conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Address Verification and Validation
These are two related but distinct processes in which the system takes the multi-field address provided by a user and parses it against curated reference data. Simply put, address verification is the process of determining whether an address entered by a user actually exists. Address validation, on the other hand, is the process of determining whether the address is mailable, meaning it can be used for postal purposes. In other words, verification covers both postal and non-postal addresses, while validation is a subset that focuses only on postal addresses.
Both are machine-to-machine processes by which data is cleaned up, and both are essential for eliminating bad addresses and maintaining the quality and reliability of address databases. Precisely’s system uses Universal Postal Union standards to verify address and meet requirements globally, and can verify addresses over 250 countries/territories across different language and character sets.
Geocoding
For some use cases, having an accurate, verified address is enough, but for many industries, real-world positional accuracy is also essential. Delivery and emergency services obviously need this information, but so do insurance companies, for example, which need to know how close a property is to a river or a forest to calculate flooding or fire risks. Addresses therefore need to be linked to a physical location in the world through geocoding. Geocoding is the process of assigning hyper-accurate latitude/longitude coordinates to every address, and attaching a unique ID to it: the PreciselyID.
The PreciselyID
Previous articles in this series have discussed some of the issues with traditional addresses. Multi-field address labels do not fit neatly into our computer systems; US addresses have 13 individual attributes—globally, there are a total of over 300 attributes. Furthermore, addresses change over time. Precisely’s answer to these problems is the PreciselyID: a single, unique and versatile identifier assigned to every addressable location.
Replacing multiple address fields with a single code means the PreciselyID is easier to incorporate into digital infrastructure, more reliable, and more versatile than a multi-field address. It is also permanent and future-proof, as it continues to represent the same location regardless of changes to structure, road names, post codes, or other factors.
Source: Precisely
Location Intelligence through Data Enrichment
However, perhaps the most exciting aspect of Precisely’s system is the fact that it enables users to enrich the data with additional context, allowing them to derive additional insights or location intelligence (LI), and to identify relationships between addresses.
Data Enrichment
By using the PreciselyID identifiers, address databases can be connected to a catalogue of additional information, enhancing both the accuracy and utility of address data for a variety of uses. Addresses can be enriched with over 400 datasets containing more than 9,000 attributes, including points of interest, neighbourhood details, property characteristics, weather data and more. This data enrichment delivers the context necessary to create data-driven strategies based on things like demographics, crime risk, or which houses present opportunities for insurance policies.
The metadata also contains primary and secondary address data—for instance, a primary address like ‘100 Main St’ may have numerous secondary addresses, or ‘children,’ in terms of individual apartments. Metadata can reveal previously unknown relationships like this between address data.
By generating and delivering this metadata, Precisely’s advanced Geo Addressing supports in-depth analysis, and enhances automated decision making. Metadata can also be shared between companies for even greater utility, and third-party data sets can be run through Precisely’s service, to clean up data for machine learning functions, for example.
Unleashing the Potential of Geo Addressing Technology
Precisely’s Geo Addressing solutions are at the forefront of address management, meeting the demand for accurate, reliable, and versatile address data, and providing businesses with the tools they need to navigate the complexities of an increasingly interconnected world.
The comprehensive features of Precisely’s Geo Addressing system offer multiple benefits across various sectors. The system provides improved accuracy, ensuring that address data is accurate and up-to-date, reducing errors and improving overall data quality. It increases operational efficiency by streamlining address entry, verification, and validation processes, saving time and resources for businesses. Perhaps most importantly, it enables enhanced, data-driven decision making, by providing businesses with enriched data and location intelligence.
In our final article, we will focus in more detail on the practical applications of Geo Addressing across different sectors, illustrating how these solutions are transforming industries and meeting diverse needs.
Did you like the article about Geo Addressing System? Read more and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!