Have you ever found yourself in this scenario? You’re riding a bike or driving a car, eager to know where to go at the next intersection, but each glance at your map distracts you from the road, making you feel quite unsafe.
Navigating by vehicle or bicycle often necessitates these distracting glances at maps. Balancing your focus between the road and checking directions is a challenge, leading to cumbersome and potentially dangerous situations. This divided attention highlights a pressing demand for more intuitive navigation solutions.
What about a solution that allows you to navigate without shifting your gaze to another device? If you share this need, augmented reality (AR) smart glasses might be the answer for you.
AR Smart Glasses Providers
With the advent of devices like Apple Vision Pro, interest in spatial computing is growing, drawing attention to augmented reality as a transformative tool. Before delving deeper, it’s important to distinguish between three distinct concepts:
- Augmented Reality (AR): Overlays virtual information onto the real world.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Blends physical and digital elements seamlessly
- Virtual Reality (VR): Immerses users in a completely virtual environment.
To gain a comprehensive understanding, we need to look at the types of AR glasses available today. Current AR glasses can be broadly categorized into two types:
- Integrated AR glasses are standalone ultra-lightweight devices. They have reached a consumer-ready level with reduced size and weight for mass production, making them ideal for navigation scenarios.
- Split-unit AR glasses are devices with mobile host boxes. They can enhance interaction and enable manufacturers to build early operating systems and content ecosystems. However, balancing functionality and portability in mobile scenarios remains a challenge.
In the following sections, we will explore the leading AR glasses manufacturers, their innovative products, and how they shape AR navigation’s future and beyond.
Google AR Glasses: Pioneer in AR Glasses
Google has been a pioneer in the field of augmented reality (AR) technology, with its journey marked by both innovation and hurdles.
The company first ventured into the AR glasses market in 2012 with a wireless device. The device featured a small, specially designed lens mounted at the top right corner of the right eyeglass frame. However, the display was limited to basic interactions like checking the weather, navigation, and making calls. Despite the initial excitement, Google discontinued the consumer version of Google Glass in January 2015 due to privacy concerns, design criticisms, and limited functionality.
Continuing its efforts, Google introduced the Google Glass Enterprise Edition, targeting business applications. Released in 2019 and priced at $999, this improved version offered features tailored for professional use, such as a voice-controlled interface for hands-free operations in industrial settings. Companies like DHL and Boeing reported increased productivity by integrating Google Glass into their workflows.
Despite the promising features, Google faced setbacks with its AR glasses. The Enterprise Edition was also discontinued in March 2023. Google’s repeated attempts to establish a foothold in the AR glasses market. However, due to various challenges such as market competition and timing issues, they have often been short-lived.
At Google I/O 2024, new Geospatial AR features for Google Maps and updates to AR development tools were introduced. This indicates that Google continues to innovate in AR technology, though concrete plans for a new AR glasses launch remain unclear.
As the company continues to refine its technology and explore new applications, the future of Google AR glasses remains a topic of keen interest in the tech community.

Glass Enterprise Edition 2, source: Google
Rokid: Improve Spatial Viewing Experience
Rokid, founded in China, in 2014, has quickly established itself as a significant player in the AR glasses market. In January 2020, Rokid launched China’s first consumer-grade AR glasses, the Rokid Glass 2, and continued to innovate with products like the Rokid Max and Rokid Air Pro, designed for cultural tourism and broader consumer use.
In April 2024, at the Rokid Open Day, Rokid introduced the Rokid AR Lite spatial computing suite, featuring the Rokid Max 2 and Rokid Station 2. This suite utilizes optical see-through (OST) technology, making the glasses exceptionally lightweight at just 75 grams. The Rokid Max 2 also features a new control system, replacing traditional remote controls with a “mini smartphone” interface that combines touch and physical buttons for intuitive interaction.
Regarding interaction, the Rokid AR Lite has moved away from the single-eye camera and gesture interaction system used in previous models. It has also eliminated physical buttons on the front of the main unit, introducing a gesture touch mode alongside the spatial ray mode.
Rokid chose to cooperate with Vivo, integrating the spatial video content shooting capabilities provided by Vivo. Compared to XREAL’s self-developed AR host approach, Rokid’s partnership with Vivo offers a more convenient path for content creation and distribution.
According to Kickstarter, the early bird prices are as follows: Station 2 at $199, Max 2 at $359, and the Rokid AR Lite suite at $479.

Rokid AR Max, Source: Rokid
XREAL: Enhance Movie and Entertainment Experience
XREAL, originally known as Nreal, is a prominent AR glasses brand under Unicron Technology, founded in 2017 in Beijing. In August 2020, XREAL launched the Nreal Light, the first AR glasses capable of connecting to mobile phones.
In May 2023, the company officially rebranded to XREAL. They launched the products including the Xreal Air and Xreal Air 2, lightweight AR glasses designed for everyday use. These devices offer a large virtual display, ideal for media consumption.
XREAL has been focusing on creating a comprehensive content ecosystem for AR, including mobile applications, wireless entertainment, and AR-native content. In an effort to address the lack of content in the AR field, XREAL introduced the Beam Pro on May 30th, 2024, a computing terminal designed to transform 2D applications into 3D spaces. This device aims to seamlessly integrate a rich array of content, from mobile apps to living room entertainment, into the AR experience.
In the Chinese market, XREAL has continued its strategy of simplification with the Beam Pro, emphasizing its “pocket giant screen” concept, and focusing primarily on enhancing the movie and entertainment experience.

XREAL Beam, Source: XREAL
RayNeo: AR Navigation in Over 100 Countries
RAYNEO, supported by TCL Electronics in China, was established in October 2021 and quickly gained recognition in the AR market.
In October 2021, RayNeo launched its first consumer-grade AR glasses. By October 2023, they had introduced the RayNeo X2, a groundbreaking AR device featuring dual-eye full-color MicroLED waveguide displays.
The RayNeo X2 offers a seamless blend of AR features, such as intelligent GPS navigation that updates in real-time as users move. It is also capable of audio and video calls, real-time AI translation, music playback, and first-person video recording.
Additionally, it integrates with Amap and HERE for navigation, supporting map data from over 100 countries and featuring intuitive spatial arrow guidance and real-time road information updates.
MYVU: Lightweight and Automotive Integration
MYVU is an AR glasses brand launched by DreamSmart, known for its innovative and user-friendly designs. DreamSmart’s strategy is Mobile (Meizu) + XR (MYVU) + Smart Car (Polestar). The MYVU series includes two models: the consumer-oriented MYVU and the MYVU Discovery Edition.
The consumer version of MYVU, features a dual-eye design with single-color Micro-LED. Weighing only 43 grams, these AR glasses are extremely lightweight and designed for everyday use. The glasses also incorporate resin waveguide lenses, which provide a high light transmission rate of up to 90%.
The MYVU Discovery Edition, priced at ¥9999, represents a significant leap in AR technology with full-color Micro-LED and diffractive waveguide technology. This model features the world’s first mass-produced full-color resin diffractive waveguide lenses, which are lighter and more durable than traditional glass lenses. The frames are made from aluminum-magnesium alloy, using a lightweight, hollow design, and weigh only 71 grams, making them the world’s lightest dual-eye full-color AR glasses.
MYVU has set a new standard in the AR industry with its focus on lightweight design. Compared to other AR glasses, MYVU has a strong connection to car companies such as Geely, Polestar, and Lynk & Co. This strategic alliance may enhance the user interaction experience in driving scenarios, offering better integration and usability for drivers.

MYVU Navigation, Source: MYVU
VUZIX: Enterprise Applications
Vuzix is a prominent player in the AR industry, known for its standalone ultra-lightweight devices that cater to both consumer and enterprise applications. But it has a strong focus on enterprise scenarios.
For enterprise applications, Vuzix offers the Vuzix Blade Upgraded headset. This device is designed to provide remote access to multimedia content, particularly beneficial for field technicians and production line workers.
The Vuzix Blade 2 takes AR to the next level with its commercial-grade design, aimed at industrial applications. It is one of the few AR glasses that meet ANSI Z87.1 eye protection standards, making it suitable for hazardous locations and factories.
Vuzix products are known for their durability and functionality, making them invaluable tools for building a connected workforce.

VUZIX BLADE 2, Source: VUZIX
META: Not Now, But Coming Soon!
Partnering with the iconic eyewear brand Ray-Ban, Meta introduced their glasses series, starting with the Ray-Ban Stories. These glasses do not feature a display but offer functionalities such as voice interaction with Meta AI, enhancing their utility and user experience.
The second generation, Ray-Ban Wayfarer, has shown significant improvements over its predecessor. Key upgrades include:
- Enhanced voice interaction and improved audio quality
- Improved heat management
- 1080p video capture at 30fps
- 32GC build-in memory, storing up to 500 photos or 100 short videos
- Feature a 12-megapixel wide-angle camera, capable of capturing high-quality photos
Priced from $299, the Wayfarer series has been a commercial success, with over 1 million pairs sold, often selling out on both the Ray-Ban and Meta websites.
Looking ahead, Meta’s AR glasses prototypes, codenamed Project Nazare and Project Aria, are expected to offer advanced features such as a wide field of view with AR overlays, a sleek and stylish form factor, holographic displays with built-in projectors, and multiple sensors. These prototypes are designed to provide an immersive AR experience with functionalities like radio, speakers, and cameras, all within a thin profile of less than 5mm and a battery life of up to 4 hours.
Meta’s CTO, Andrew Bosworth, has indicated that the company’s most advanced AR glasses prototype could be released as early as late 2024. This prototype promises to be a groundbreaking consumer electronics device, integrating sophisticated AR functionalities with a sleek design. Meta’s roadmap suggests that the first generation of these AR glasses, rumored to launch in 2025, will initially focus on smart glasses capabilities before fully transitioning into immersive AR experiences. In addition to their work on AR glasses, Meta has made significant advancements in the VR space with their Meta Quest series.
Others: Companies to Look Out For
Several other companies are also making significant advancements in the market, such as LA.WK, Magic Leap, INMO, and those from large smartphone companies like Huawei and Xiaomi.
LA.WK, for instance, has introduced the Meta Lens Chat AI glasses, powered by its large language model WAKE-AI. These glasses offer navigation through the built-in system, which uses Baidu Maps to provide real-time directional guidance via the glasses’ speakers.
Additionally, there are outdoor professional AR glasses like the QIDI Vida, which utilize AR HUD displays. These glasses display essential information such as battery status, navigation, and positioning guidance. Users can customize the data display and focus on the road ahead.
In the VR realm, notable brands include Apple Vision Pro, PICO, and Microsoft HoloLens. These devices are generally too heavy for navigation use, as wearing a device weighing over 500 grams for extended periods is impractical.
Given the weight and bulk of many VR headsets, they are more akin to helmets than glasses, which limits their practicality for navigation scenarios. For navigation, lightweight AR glasses weighing less than 100 grams can offer a better balance of functionality and comfort.

Outdoor Augmented Reality Navigation, Source: QIDI Vida
Challenges in AR Smart Navigation: Balancing Innovation and Practicality
Despite the promising potential of Augmented Reality navigation, several challenges need addressing to fully realize its capabilities.
These challenges span across hardware, display technologies, AR mapping techniques, battery life and weight, network connectivity, intuitive interaction methods, and the seamless transition between indoor and outdoor navigation.
Achieving a balance between appearance, display, performance, and battery life is another area of focus.
Spatial Computing
Spatial positioning and computing are critical components of AR navigation, relying on:
- Intelligent recognition technologies
- SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)
- Multi-sensor platforms (cameras, accelerometers, biometric sensors)
- Networking and edge computing
These technologies enable the seamless merging of virtual images and 3D models with the real world, crucial for both indoor and outdoor navigation. However, achieving precise positioning and real-time mapping, especially in varying environments, remains a significant challenge.
Eye Tracking
Eye tracking can enhance the user experience by:
- Adjusting displays based on eye movements
- Improving interaction precision
- Reducing eye strain by minimizing the need for constant refocusing
Effective eye tracking keeps virtual overlays in sync with the user’s line of sight, making the AR experience more natural and immersive.
High-precision eye tracking is costly and technically challenging. AR devices rarely include high-precision eye tracking. It is primarily found in XR devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Microsoft HoloLens. Companies like Tobii are working to make this technology accessible and cost-effective.
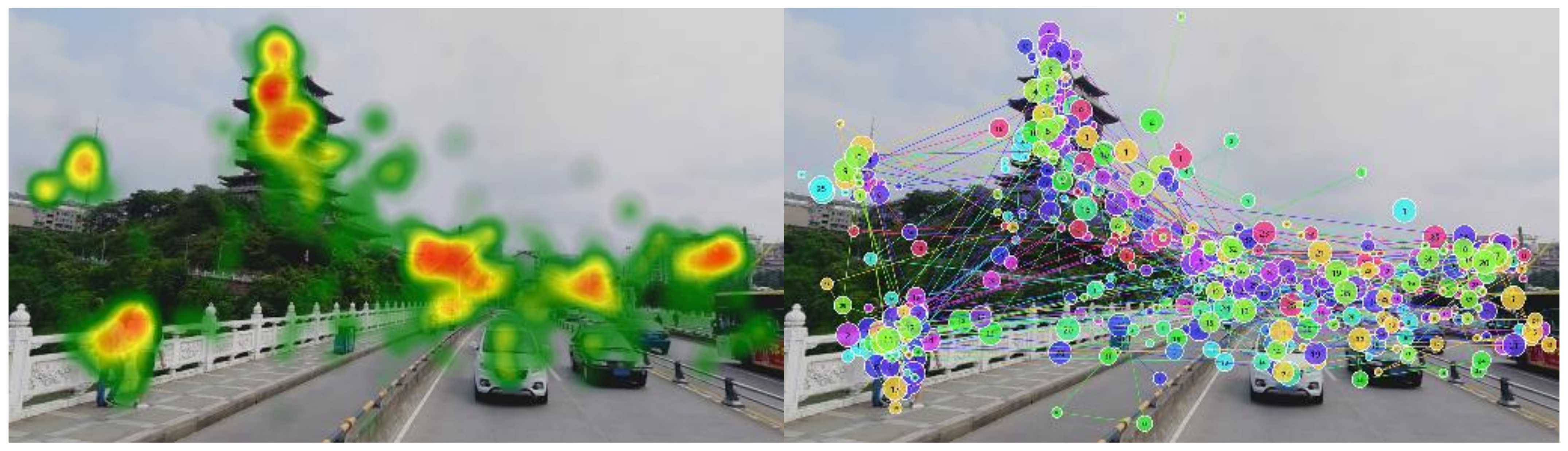

Eye-tracking Example Picture showing a heat map and track map, Source: MDPI
Interaction Methods
Intuitive interaction methods are also crucial. Most current AR systems rely on complex gestures or external controllers, which are cumbersome. Advances in natural user interfaces, such as voice control, eye tracking, and hand gestures, are essential for making AR glasses more user-friendly.
AR glasses utilize a range of interaction methods to offer a seamless and intuitive user experience. These methods include rings, touch controls, applications, and AI voice commands.
- Interaction rings
- Connect via Bluetooth
- Feature touchpads, buttons and gyroscopes
- Support 3DoF interaction
- Touch controls on glasses frames
- Smartphone application integration
- AI voice assistants
- Enhanced by large language models like ChatGPT
- Offer fast recognition, high accuracy, and personalized responses
- Enable natural, conversational interactions
In conclusion, while AR navigation holds significant promise, addressing these technical challenges is essential for developing practical and user-friendly AR glasses. Ongoing research and technological advancements in hardware, display technologies, power management, connectivity, interaction methods, and mapping techniques are paving the way for the next generation of AR navigation solutions.
Market and Applications of AR
Augmented Reality applications extend beyond navigation, enhancing spatial memory, perception, and mapping capabilities. This revolutionizes geospatial data visualization and user interaction, transforming how we navigate and interact with the world.
Key applications include emergency evacuation guidance, providing real-time guidance by displaying escape routes and safety instructions directly in the user’s field of view.
For indoor object location, AR enhances the ability to find items by overlaying directional cues and information on the real-world environment, making it easier to locate specific objects.
Additionally, AR devices assist in spatial tasks by providing contextual information and visual cues, improving users’ ability to remember and navigate complex spaces.
The AR market is experiencing rapid growth, with a global market size valued at USD 62.75 billion in 2023. Projections indicate that by 2028, this market will exceed $97 billion. This growth is driven by significant investments and technological advancements from major tech companies. Integrating AR and navigation functions is expected to open up even broader market opportunities in the coming years, as adoption increases across consumer and industrial sectors.
Did you like the article? Read more and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!